Abstract
Angioid streaks are a striking fundus change produced by linear breaks in Bruch’s membrane. First described in 1889 by Doyne in a patient with retinal hemorrhages secondary to trauma. They are most often associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum, but there have been a number of cases reported in connection with other conditions, such as Paget’s disease, which is a localized disorder of bone remodeling characterized by the increase in bone resorption followed by an increase in new bone formation, altering bone architecture. Angioid streaks are present in 10 to 15% of patients with Paget’s disease. It was aimed to share this case report to underline the rarity of this combination.
Keywords: Angioid streaks; Paget’s disease; Choroidal neovascularization
Introduction
Angioid streaks are often associated with a systemic condition, most frequently pseudoxanthoma elasticum, Paget’s disease and sickle-cell anemia. They are described as visible, linear, irregular, cracklike dehiscences of Bruch membrane, which may be unilateral or most commonly bilateral. Several diagnostic methods are useful to diagnose, evaluate, and monitor angioid streaks, and various treatment modalities have been used, with promising results.
The purpose of this case report is to review the literature on angioid streaks, and to highlight pathophysiology, clinical presentation, imaging, and treatment modalities for angioid streaks.
Case Report
F.A. a woman aged 41, She was small with the typical bowing of the legs and enlargement of the head characteristic of Paget's disease (Figure 1). She had no ocular complaints. She came for a routine eye examination. The ocular findings were as follows: Best-corrected visual acuity was 20/20 bilaterally. External ocular examination was normal. Examination of the fundus in both eyes showed an irregular halo of choroidal depigmentation surrounding the nerve head, with brownish linear irregularities extending radially from the peripapillary region into the peripheral fundus a finding consistent with the presence of angioid streaks (Figure 2). In autofluorescence, they appeared hypoautofluorescent (Figure 3). Simple observation was our treatment option since there was no complication such as choroidal neovascularization.
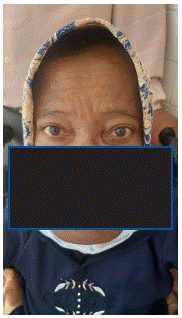
Figure 1: Clinical photograph showing facial deformities of the patient, including enlargement of the skull; broadened forehead; swelling in the maxilla, the mandibular ramus, and the mandibular angle; characteristic of Paget’s disease.
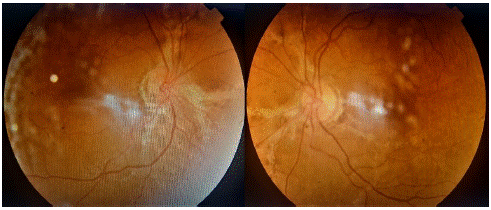
Figure 2: Color fundus photograph in both eyes: angioid streaks emanating from the optic nerve.
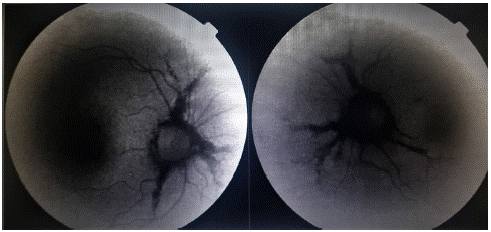
Figure 3: Autofluorescence imaging in both eyes: Angioid streaks visible as irregular lines of reduced autofluorescence running outwards from the optic discs.
Discussion
During these last years, a large number of articles have been published on the retinal angioid streaks. They are most frequently associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum [1]. However, a number of cases have been reported in association with other diseases, such as Paget's disease, a chronic progressive disease of the bone of uncertain etiology, characterized initially by an increase in bone resorption, followed by a disorganized and excessive formation of bone. This association was first described by Batten and Verhoeff in 1931 [1]. Studies by Terry, Scholz and Berliner indicate that between 10 and 15% of patients with Paget’s disease show evidence of angioid streaks; their incidence is greater in patients with early age onset of symptoms, skull involvement, and an active systemic disease as demonstrated by markedly elevating serum alkaline phosphatase and urinary hydroxyproline. Many ocular manifestations of Paget's disease have been published, such as Pigmented spots, streaks of pigment, arteriosclerosis, retinal and choroidal hemorrhages, and in advanced cases, cataracts and compressive lelesions of the optic nerve was present, and they are usually due to bony changes in the skull and narrowing of the optic foramen [2]. The bone deformities in Paget’s disease lead to calcium binding on the elastic fibers that occupies the mid segment of Bruch’s membrane, resulting in disintegration and frying of the elastic fibers leading to angioid streaks.
They are usually bilateral and asymptomatic, with asymmetrical involvement of the two eyes, symptoms appear when the foveola is involved, in case of Choroidal Neovascularization (CNV) in the macula, or traumatic Bruch’s membrane rupture. The diagnosis is most often made on the basis of fundus examination, but Fluorescein angiography may be useful if the presentation is subtle. Angioid streaks have a "window defect" due to atrophy of RPE adjacent to them. Leakage of fluorescein is evident if CNV is present. Autofluorescence is a practical tool to confirm the diagnosis and to evaluate the evolution. They appear hypoautofluorescent due to attenuated or absent RPE in angioid streaks. Optical coherence tomography is also useful evaluate angioid streaks and the CNV.
Many treatment procedures have been used for the treatment of CNV, the commonest and most serious complication secondary to angioid streaks, However, until recently, they only limit the natural course of the disease without definitive inactivation [2]. There is no indication for prophylactic treatment of angioid streaks. In fact, some researchers believe that this kind of intervention can actually induce CNV. Photocoagulation was used in the past for juxtafoveal and extrafoveal lesions. But it leaded to retinal hemorrhages, degenerative changes, and loss of central vision. Since then, there are several case series, presenting controversial results. ICG-mediated photothrombosis was also used for subfoveal CNV with preservation of visual acuity and anatomical improvement [3] Transpupillary thermotherapy has been also used without any positive effect on disease progression [4,5]. Other procedures such as Macular translocation and subretinal extraction have been also used but has been abandoned considering the recurrences and adverse events [6,7]. The use of Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) with verteporfin in several studies and case reports had encouraging results, while other studies present contradictory results [8-15]. Intravitreal injection of anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) may be a promising treatment. In many studies, intravitreal bevacizumab was found to mildly reduce central foveal thickness and stabilize visual acuity [16-18].
The prognosis is poor without treatment, a disciform scar may occur in case of CNV at the fovea. Risk factors for a worse final visual outcome are the age at the initiation of symptoms, the localization of CNV regarding to the fovea, and the presence of a concomitant eye disease.
Conclusion
The discovering of angioid streaks on fundus examination should draw attention on the systemic conditions which may be present. And should lead to several investigations to evaluate, and monitor angioid streaks, and to diagnose macular choroidal neovascularization, which is the main cause of visual impairment
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Contribution of the authors
All the authors participated in the care of the patient and the writing of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
References
- Georgalas I, Papaconstantinou S, Koutsandrea C, Kalantzis G, Karagiannis DA, et al. Angioid streaks, clinical course, complications and current therapeutic management Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management. 2009; 5: 81-9.
- Chatziralli I, Saitakis G, Dimitriou E, Chatzirallis A, Stoungioti S, et al. Review: ANGIOID STREAKS A Comprehensive Review From Pathophysiology to Treatment. Retina. 2019; 39: 1-11.
- Malerbi FK, Huang SJ, Aggio FB, Carvalho E, Bonomo PP, et al. Indocyanine green mediated photo thrombosis for choroidal neovascularization in angioid streaks. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2008; 71: 311–315.
- Aras C, Baserer T, Yolar M, Yetik H, Artunay O, et al. Two cases of choroidal neovascularization treated with transpupillary thermotherapy in angioid streaks. Retina. 2004; 24: 801–803.
- Ozdek S. Transpupillary thermotherapy for the treatment of choroidal neovascularization secondary to angioid streaks. Can J Ophthalmol. 2007; 42: 95–100.
- Roth DB, Estafanous M, Lewis H. Macular translocation for subfoveal choroidal neovascularization in angioid streaks. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 131: 390–392.
- Ehlers JP. Treatment of non age-related macular degeneration submacular diseases with macular translocation surgery. Retina. 2011; 31: 1337–1346.
- Elías-de-Tejada M, Calvo-Gonzalez C, Reche-Frutos J, Donate-Lopez J, Garcia-Sanchez J, et al. Photodynamic therapy in angioid streaks. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2007; 82: 741–746.
- Heimann H, Gelisken F, Wachtlin J, Whner A, Volker M, et al. Photodynamic therapy with verteporfin for choroidal neovascularization associated with angioid streaks. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005; 243: 1115–1123.
- Arias L, Pujol O, Rubio M, Caminal J. Long-term results of photodynamic therapy for the treatment of choroidal neovascularization secondary to angioid streaks. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006; 244: 753–757.
- Shyong MP, Chen SJ, Lee FL, Tsao YP, Hsu WM, et al. Increased and persisted subretinal haemorrhage after photodynamic therapy for choroidal neovascularization secondary to angioid streaks. Eye (Lond). 2006; 20: 1420–1422.
- Jurklies B, Bornfeld N, Schilling H. Photodynamic therapy using verteporfin for choroidal neovascularization associated with angioid streaks–long-term effects. Ophthalmic Res. 2006; 38: 209–217.
- Schargus M. Photodynamic therapy in classic chorioidal neovascularisation in patients with angioid streaks [in German]. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2006; 223: 987–992.
- Lee JM, Nam WH, Kim HK. Photodynamic therapy with verteporfin for choroidal neovascularization in patients with angioid streaks. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2007; 21: 142–145.
- González-Blanco MJ, Blanco-Rivera C, Campos-García S. Treatment of angioid streaks with phothodynamic therapy. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2007; 82: 719–722.
- Neri P, Salvolini S, Mariotti C, Mercanti L, Celani S, et al. Long-term control of choroidal neovascularization secondary to angioid streaks treated with intravitreal Bevacizumab (Avastin(R)). Br J Ophthalmol. 2008; 93: 155-8.
- Wiegand TW, Rogers AH, McCabe F, Reichel E, Duker JS. Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) treatment of choroidal neovascularization in patients with angioid streaks. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008; 93: 47-51.
- Donati MC, Virgili G, Bini A, Giansanti F, Rapizzi E, et al. Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) for choroidal neovascularization in angioid streaks: A case series. Ophthalmologica. 2008; 223: 24–27.
