
Case Report
Austin J Urol. 2015; 2(4): 1035.
Leiomyoma of Urinary Bladder Presenting as Acute Urinary Obstruction: Report of 2 Cases
Mehta N, Rathore RS, Bansal D, Babu M, Pillai B, Sam MP and Krishnamoorthy H*
Department of Urology, Lourdes Hospital, India
*Corresponding author: Krishnamoorthy H, Department of Urology, Lourdes Hospital, Ernakulam, Cochin, Kerala- 682012, India
Received: August 14, 2015; Accepted: November 25, 2015; Published: December 05, 2015
Abstract
Leiomyomas of the bladder are rare (0.43% of bladder neoplasms); however, they are the most common benign bladder tumors. Patients present with a wide age range, spanning from 20 to 80 years, and equal incidence between men and women. Most lesions are small and asymptomatic. Larger lesions typically present with symptoms caused by mass effect or urinary obstruction, such as hesitancy, frequency, and hematuria. Although these tumors originate from the submucosa, growth may be intravesical (63%), extravesical (30%), or intramural (7%). Cystoscopy, ultrasound, Omography or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can be used in the diagnosis, but the definitive diagnosis is made by histopathology. There is not a single case of malignant transformation in bladder leiomyomas. The traditional treatment for symptomatic cases is surgical resection. The most important determinants for the choice of surgery are tumour size, localization and its involvement of urinary sphincter or ureter orifices. We report cases of 2 female patients who presented to us with acute urinary retention. Abdominal Ultrasound and Computed tomography showed solitary bladder tumour. Diagnostic cystoscopy with Transurethral Resection (TUR) was done for both the patients. Histopathological examination confirmed the diagnosis of leiomyoma of urinary bladder.
Keywords: Bladder tumour; Leiomyoma; Acute urinary retention
Case Presentation
Case 1
63 year old female patient presented to us with acute retention of urine. Patient had no known comorbidities. Her physical examination and blood investigations were normal. Ultrasound of the abdomen revealed a solitary mass lesion within the urinary bladder of size 4 x 3 cm with normal upper tracts. Computed Tomography (CT) showed a well circumscribed pedunculated solitary mass of 4.3 x 4 cm on the left lateral wall of the urinary bladder. Cystoscopy with TUR was done. The histology of resected tumour came back as showing a leiomyoma (Figure 1).
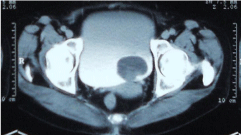
Figure 1: (Case 1) Pedunculated leiomyoma of bladder.
Case 2
A 43-year-old female normally fit and well who was referred with acute retention of urine. She had a history of a single episode of hematuria. She was investigated with an abdominopelvic ultrasound which showed a vascular 5.5 x 5 cm mixed echogenic rounded mass lying centrally within the urinary bladder. CT scan revealed a large, moderately enhancing, solitary centrally placed mass within the bladder with bilateral moderate hydroureteronephrosis. Cystoscopy with TUR was done. Cystoscopy showed a large intravesical tumour with intact mucosa. Biopsy of the mass disclosed a submucosal neoplasm composed of fascicles of smoothmuscle proliferation with focal hyaline and microscopic degeneration suggesting a leiomyoma. Both the patients voided well after catheter was removed postoperatively (Figure 2).
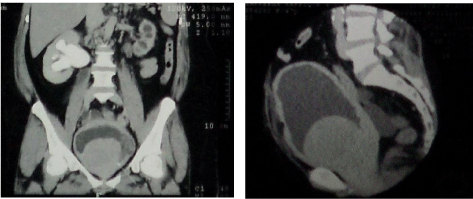
Figure 2: (Case 2) Large, centrally placed intravesical leiomyoma.
Discussion
Leiomyomas are the most common non epithelial benign tumours of the bladder composed of benign smooth muscle [1]. It accounts for about 0.43% among all bladder tumours [2]. Most bladder tumors originate from the epithelium; however, leiomyoma of the bladder has a mesenchymal origin. Bladder leiomyomas can be asymptomatic and are frequently found incidentally by pelvic ultrasonography. Leiomyoma has its origin from the smooth muscle bundles and contains connective tissue surrounding it. Therefore it can arise in any organ which contains this tissue. Kidney and bladder remain the most frequent sites of origin of these tumours amongst the genitourinary tract [3]. It is more common in females of fertile age group, with a female/male ratio of 5: 2 and its peak incidence is between 4th and 5th decades of life. The first bladder leiomyoma was reported in 1931, and after that about 250 cases have been reported [5]. There are many proposed etiologies for leiomyoma, including chromosomal anomalies, hormonal changes, infection of bladder smooth muscle, perivascular inflammations and disonthogenesis [6]. Macroscopically, these are round or oval tumours with an elastic consistency and an irregular surface. The size is variable with reports of tumour sas big as 30cm, especially in the extravesical localization. Bladder leiomyomas are known to produce symptoms, dependent on their location primarily and, secondarily, their size. They are known to occur endovesically, intramurally, and extravesically, with a frequency of 63%, 7%, and 30%, respectively. Of these types, the endovesical type more frequently causes obstructive or irritative urinary symptoms [7]. In bladder lesions, the localization is submucosal in 63%, and cystoscopy shows a sessileor pedunculated lesion covered by normal mucosa. The subserosal localization represents 11-30% of the cases, having a characteristic pedicle that bounds it to the bladder. The intramural localization is the less frequent and represents 7-17% of the cases, seen as a well encapsulated tumour in the bladder wall. Endoluminal tumours are more symptomatic, presenting with urinary tract infections, hematuria, irritative symptoms, especially the ones at the bladder neck, or obstructive symptoms, causing even acute bladder outlet obstruction secondary to a valve effect. Intramural and subserosal tumors are in general asymptomatic and the diagnosis is incidental. When the size is considerable it can appear as a pelvic mass or give symptoms secondary to the compression of adjacent structures. Leiomyomas can be diagnosed preoperatively by radiological imaging. Ultrasound allows to define the solid or cystic nature of the lesion, showing in these cases a solid smoothwall lesion with homogeneous echoes. It also allows to define the limits between the tumor and adjacent structures, showing its localization in the bladder wall. Transvaginal ultrasound is an excellent option in female posterior bladder wall tumours in subserosal localization [8]. Computed tomography gives us information about the size, position, and relationship between the tumour and bladder wall. Cystic components indicate degeneration or necrosis. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is superior to CT for characterization, better demonstrating their submucosal origin and muscular preservation [9]. T1WI demonstrates intermediate signal intensity, whereas T2WI shows low signal intensity. In the presence of cystic degeneration, high signal intensity may be seen on T2WI. Enhancement is variable following contrast administration. There is no radiological test that allows us to differentiate a leiomyoma from leiomyosarcoma, therefore pathologic diagnosis is mandatory. Pathological analysis reveals proliferation of smooth muscle fibers with an eosinophilic cytoplasm with less than two mitotic figures per power field. They are surrounded by a variable amount of connective tissue and there are no necroses or cellular atypia. Immunohistochemically, most leiomyomas of the bladder exhibit strong diffuse immunoreactivity for smooth muscle actin, muscle-specific actin, desmin, and vimentin and are usually negative for cytokeratin and S100 protein [10]. Other tumors that arise in the bladder wall include neurofibroma, sarcoma, paraganglioma, pheochromocytoma and lymphoma. Traditionally, bladder leiomyomas have been treated by surgical resection. The tumor size, extent, and location and the involvement of the sphincter or ureters determine the route of resection. Small endovesical tumor scan be managed with TUR and fulguration. Larger endovesical, intramural, or extravesical tumors will be managed best with segmental resection. TUR, segmental resection or partial cystectomy, transvaginal excision, laparoscopic partial cystectomy, and, recently, robotic-assisted laparoscopic excision have all been successfully used for bladder leiomyoma removal [7,11,12]. Prognosis is good and recurrence is rare if the resection is adequate, therefore it seems not to be necessary to establish follow up protocols.
Conclusion
Leiomyoma of the urinary bladder is a rare disorder that occurs more frequently in women. These tumors can be treated successfully using varying surgical approaches, and the prognosis is good after complete resection. Although imaging and cystoscopic evaluations can aid in the diagnosis, surgical excision is the best option for confirmation of the diagnosis, as well as for treatment of the disorder.
References
- Goluboff E, O’Toole K, Sawczuk I. Leiomyoma of bladder: Report of case and review of literature. Urology. 1994; 43: 238-241.
- Casares FJB, Sanfelipe SJ, Servio IL, Cadira JLB, Marcellan FJR. Characteristics of bladder leiomyoma in our setting. Arch Esp Urol. 1995; 48: 987-990.
- Belis JA, Post GJ, Rochman SC, Milam DF. Genitourinary leiomyomas. Urology. 1979; 13: 424-429.
- Aristu JIJ, Uruñuela FL, de Pablo Cárdenas A, Paul MAP, Calvo JJ, Semper MM, et al. Leiomyoma of the bladder. Report of a case. ActasUrol Esp. 2001; 25: 223-225.
- Kretschmer JL. Leiomyoma of the bladder with a report of a case and a review of the literature. J Urol. 1931; 26: 575-589.
- Teran AZ, Gambrell RD Jr. Leiomyoma of the bladder. Int J Fertil. 1989; 34: 289-292.
- Knoll LD, Segura JW, Scheithauer BW. Leiomyoma of the bladder. J Urol. 1986; 136: 906-908.
- Kabala JN, Freiha FS, Niebel JD. Leiomyoma of the bladder: Report of two cases and demonstration of ultrasonic appearance. Urology. 1990; 35: 210-212.
- Wong-You-Cheong JJ, Woodward PJ, Manning MA, Sesterhenn IA. From the Archives of the AFIP: neoplasms of the urinary bladder: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2006; 26: 553-580.
- Lott S, Lopez-Beltran A, MacLennan GT, Montironi R, Cheng L. Soft tissue tumors of the urinary bladder. Part I: myo?broblastic proliferations, benign neoplasms, and tumors of uncertain malignant potential. Hum Pathol. 2007; 38: 807-823.
- Jeschke K, Wakonig J, Winzely M, Henning K. Laparoscopic partial cystectomy for leiomyoma of the bladder wall. J Urol. 2002; 168: 2115-2116.
- Thiel DD, Williams BF, Krishna M, Leroy TJ, Igel TC. Robot-assisted laparoscopic excision of bladder wall leiomyoma. J Endourol. 2009; 23: 579-582.