
Special Article – Occupational Therapy
Phys Med Rehabil Int. 2016; 3(2): 1083.
Effectiveness of Occupational Therapy in Rehabilitation of Guillain Barre Syndrome: A Case Study
Khanzada FJ¹* and Zameer S²
¹Department of Occupational Therapy, Institute of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Dow University of Health Sciences Karachi, Pakistan
²Department of Pathology, Dow International Medical College, Dow University of Health Sciences Karachi, Pakistan
*Corresponding author: Faizan Jameel Khanzada, Department of Occupational Therapy, Institute of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Dow University of Health Sciences Karachi, Pakistan
Received: April 23, 2016; Accepted: May 16, 2016; Published: May 19, 2016
Abstract
Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS) is an autoimmune disease and first line of treatment is auto immune suppressant therapy and Occupational therapy is necessary for prevention of muscle contracture. This is a challenging syndrome which produces the symptoms of motor weakness, altered sensation and dependency in activities of daily living. Patients require intensive multidisciplinary rehabilitation plan. Occupational therapist working with multidisciplinary rehabilitation team and plays an important role in maximizing the performance in activities of daily living and enhances the chances of effectiveness in upper extremities gross and fine motor work and sensory relearning. Currently, there is a very little research occupational therapy rehabilitation of GBS thus more research is required in this area.
Keywords: Occupational Therapy Intervention; Multidisciplinary rehabilitation; Guillain Barre Syndrome
Introduction
Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS) is an autoimmune neuromuscular disorder that may affects both sexes more male prevalence is common in ages between 30 and 50 years and is a significant cause of disability [1]. This disease is usually triggered by uncommon infectious disease complications due to bacterial or viral illness, such as Campylobacter jejuni or Cytomegalovirus that provokes immune-mediated nerve dysfunction [2,3]. GBS considered being very rare but now reports suggest of its higher prevalence and worldwide incident and are often many practitioners feeling difficulty to differential diagnose GBS [4,5]. Because it is uncommon and many signs and symptoms related to other conditions and may vary person to person so it create a vacuum and needs more work. However, it instantly changes a person’s life and is characterized by the complete loss of gross and fine movement, sensory disturbance in all extremities. And inability to perform activities of daily living and vocational work for a prolonged period. Occupational therapist plays an important role in the rehabilitation of GBS use their professional expertise and engage GBS patient in occupation to restore maximum independence in activities of daily living by improving underlying deficit performance skills like strength, range of motion, motor control, sensory re-education and teaching compensatory strategies. when recovery of deficit performance areas are unlikely to be successful and improve the skills in functional performance and make great impact on the quality of life of GBS patient [6,7]. In developing countries like Pakistan, occupational therapy is rarely offered in both government and private hospitals rehabilitation center. Majority of health professional and people are unaware of the interventions occupational therapist can apply in the rehabilitation of GBS and the number of patients with GBS do not get referred in time which results in long term consequences like impairment, disability, dependency in daily life and make burden on their family and government which cannot be easily un avoided.
Case Report
Mr. M, is a 34 years old male with a confirmed diagnosis of Acute Motor and Sensory Axonal Neuropathy, Guillain Barre Syndrome. He was referred by physiatrist Department of occupational therapy, Dow university hospital for occupational therapy to improve his range of motion, muscle strength and sensory re-education in upper limbs and to increase independence in activities of daily living.
Occupational Therapy Evaluation
Initially occupational therapy evaluation showed that patient was alert, orientationed to time, place, person and higher functions were within normal limits. Dull pain and hypo-reflexes in all extremities, proprioception was impaired. Numbness and tingling sensation was found in all extremities. Goniometry measurements of the upper limb showed that there is limitation of all active and passive range of motion in different joints (Table 1). There was flaccid paralysis, manual muscle strength examination was performed and different muscle grading is poor and traces (Table 2). On the Modified Barthel Index scale scoring was used to assess the functional ability and patient total score eighteen out of one hundred, mean patient is totally dependent in self-care and mobility (Table 3). Disturbance in perceiving the sensation of touch, sensory threshold awareness test was performed and Semmes weinstein monofilaments kit was used and stimulus ranges from 2.83 to 6.65 thresholds applied on the specific dermatome of hand and foot to mapping the sensory nerve impairments (Table 4). Scoring of the regions of S1, S2 and L5 dermatomes of foot showed that there is diminished ability to perceive light touch sensation. L3 and L4 region dermatomes of foot scores showed that patient have severe loss of protective sensation. However right and left hand C6 and C8 region dermatome scoring was also performed and showed that the patient have decreased ability to perceive deep sensations, light touch, and unable to localization sensation and feeling numbness in all limbs (Figure 1).
Upper Extremities
Pre - Active
Range of Motion
Pre – Passive
Range of Motion
Post - Active
Range of Motion
Post - Passive
Range of Motion
RIGHT
LEFT
RIGHT
LEFT
RIGHT
LEFT
RIGHT
LEFT
Shoulder Flexion
0° to 20°
0° to 25°
0° to 75°
0° to 80°
0° to 75°
0° to 80°
0° to 90°
0° to 95°
Extension
0° to 15°
0° to 20°
0° to 36°
0° to 39°
0° to 40°
0° to 45°
0° to 60°
0° to 50°
Abduction
0° to 30°
0° to 35°
0° to 90°
0° to 80°
0° to 90°
0° to 95°
0° to 105°
0° to 90°
Elbow – Flexion
0° to 25°
0° to 30°
0° to120°
0° to 110°
0° to 110°
0° to 120°
0° to 120°
0° to 140°
Forearm - Supination
0° to 15°
0° to 10°
0° to 72°
0° to 77°
0° to 75°
0° to 80°
0° to 75°
0° to 80°
Pronation
0° to 80°
0° to 79°
0° to 80°
0° to 79°
0° to 80°
0° to 80°
0° to 80°
0° to 80°
Wrist – Flexion
0° to 20°
0° to 25°
0° to 40°
0° to 45°
0° to 70°
0° to 80°
0° to 80°
0° to 80°
Extension
0° to 40°
0° to 35°
0° to 55°
0° to 61°
0° to 70°
0° to 60°
0° to 70°
0° to 67°
Fingers - Flexion
0° to 30°
0° to 33°
0° to 88°
0° to 85°
0° to 90°
0° to 95°
0° to 90°
0° to 100°
Extension
0° to 42°
0° to 43°
0° to 45°
0° to 45°
0° to 45°
0° to 43°
0° to 45°
0° to 45°
Abduction
0° to15°
0° to 20°
0° to 20°
0° to 16°
0° to 20°
0° to 20°
0° to 20°
0° to 18°
Thumb - Flexion
0°to 25°
0° to 30°
0° to 30°
0° to 30°
0° to 50°
0° to 40°
0° to 4 0°
0° to 45°
Abduction
0° to 40°
0° to 35°
0° to 42°
0° to 40°
0° to 40°
0° to 40°
0° to 50°
0° to 45°
Table 1: Active and Passive Range of Motion Pre-Post Test.
Body Joints
Movements
Muscle Groups
Measurement
Strength Grading
Pre Right
Pre Left
Post Right
Post Left
Scapula
Elevation
Upper Trapezius
1 / 5
1- / 5
4+ / 5
5 / 5
Depression
Lower Trapezius
2 / 5
1 / 5
4 / 5
4+ / 5
Retraction
Mid Trapezius
2 / 5
1+ / 5
5 / 5
4+ / 5
Protraction
Serratus Anterior
1+ / 5
1 / 5
4+ / 5
4+ / 5
Shoulder
Abduction
Middle Deltoid
1 / 5
1+ / 5
5 / 5
5 / 5
Flexion
Anterior Deltoid
1- / 5
2- / 5
5 / 5
5 / 5
Extension
Posterior Deltoid
Latissimus Dorsi
1- / 5
1- / 5
2- / 5
2- / 5
5 / 5
4+ / 5
4+ / 5
4+ / 5
Adduction
Pectoralls Major
- Clavicular
- Sternal
1 / 5
1 / 5
1+ / 5
1+ / 5
4 / 5
4+ / 5
5 / 5
5 / 5
Internal Rotation
Subscapularis
1+ / 5
2- / 5
4 - / 5
4+ / 5
External Rotation
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
1- / 5
1+ / 5
4+ / 5
5 / 5
Elbow
Flexion
Biceps (Brachioradiallas)
1 / 5
1+ / 5
5 / 5
4+ / 5
Extension
Triceps
1+ / 5
1+ / 5
5 / 5
5 / 5
Radio Ulnar
Supination
Supinators
1+ / 5
2+ / 5
5 / 5
4+ / 5
Pronation
Pronators
1- / 5
2- / 5
5 / 5
5 / 5
Wrist
Flexion
Flexor carpi radiallas
1 / 5
2- / 5
4+ / 5
4- / 5
Flexor carpi ulnaris
1 / 5
1+ / 5
4 / 5
4 / 5
Extension
Extensor carpi
radiallas longus
1+ / 5
2 / 5
5 / 5
4+ / 5
Extensor carpi ulnaris
1- / 5
1+ / 5
5 / 5
4+ / 5
Fingers
Flexion
Flexor Dig. Profundus
- Medium
- Lateral
2 / 5
2- / 5
2+ / 5
1- / 5
3 + / 5
3 - / 5
3 - / 5
3 + / 5
Flexor Dig. Superficialls
1+ / 5
1- / 5
3 + / 5
4 / 5
Extension
Extensor Digtorum
1+ / 5
2 / 5
4 + / 5
4 / 5
MCP Flexion
IP Extension
Lumbricals
2- / 5
1- / 5
1+ / 5
1+ / 5
3 - / 5
3+ / 5
4 - / 5
3 - / 5
Abduction
Dorsi Interossel
1+ / 5
1+ / 5
2+ / 5
3 / 5
Adduction
Palmer Interossel
1- / 5
1 / 5
4+ / 5
4+ / 5
Thumb
Flexion
Flexor Pollicis Longus
2- / 5
2 / 5
3- / 5
3 / 5
Flexor Pollicis Brevis
2 / 5
2+ / 5
3 / 5
3 - / 5
Table 2: Manual Muscle Testing Pre-Post Chart.
INDEX ITEM
SCORE
DESCRIPTION
CHAIR/BED TRANSFERS
0
Unable to participate in a transfer. Two attendants are required to transfer the patient with or without a mechanical device.
AMBULATION
3
Constant presence of one or more assistant is required during ambulation.
AMBULATION/WHEELCHAIR
1
Patient can propel self-short distances on flat surface, but assistance is required for all other steps of wheelchair management.
STAIR CLIMBING
2
Assistance is required in all aspects of chair climbing, including assistance with walking aids.
TOILET TRANSFERS
2
Assistance required in all aspects of toileting.
BOWEL CONTROL
2
The patient needs help to assume appropriate position, and with bowel movement facilitatory techniques.
BLADDER CONTROL
2
The patient is incontinent but is able to assist with the application of an internal or external device.
BATHING
1
Assistance is required in all aspects of bathing, but patient is able to make some contribution.
DRESSING
2
The patient is able to participate to some degree, but is dependent in all aspects of dressing.
PERSONAL HYGIENE
(Grooming)
1
Assistance is required in all steps of personal hygiene, but patient able to make some contribution.
FEEDING
2
Can manipulate an eating device, usually a spoon, but someone must provide active assistance during the meal.
Total Score
18
Total Dependence
Table 3: Modified Barthel Index Performance Scale.
Right and Left Hand Dermatome
Pre-Right Hand Monofilament Stimulus Score
Pre-Left Hand Monofilament Stimulus Score
Post-Right Hand Monofilament Stimulus Score
Post–Left Hand Monofilament Stimulus Score
T1 - Medial Arm
2.83
2.83
2.83
2.83
C5 - Lateral Shoulder
2.83
2.83
2.83
2.83
C6 - Thumb
4.56
6.65
4.31
2.83
C7 - Middle finger
2.83
2.83
2.83
2.83
C8 - Little finger
4.56
4.31
3.61
2.83
Right and Left Foot Dermatome
Pre-Right Foot Monofilament Stimulus Score
Pre-Left Foot Monofilament Stimulus Score
Post–Right Foot Monofilament Stimulus Score
Post–Left Foot Monofilament Stimulus Score
S1 -Lateral Foot
3.61
4.31
2.83
2.83
S2 -Posterior Thigh
2.83
3.61
2.83
3.61
L2 -Medial Thigh
2.83
2.83
2.83
2.83
L3 -Medial Knee
4.31
4.56
3.61
2.83
L4 -Medial Ankle
4.31
4.31
3.61
2.83
L4 -Great Toe
4.56
3.61
4.31
4.31
L5 -Dorsum Foot
3.61
3.61
3.61
2.83
Table 4: Sensory Awareness Testing Pre-Post Chart.

Figure 1:
Occupational Therapy Intervention and Results
Mr. M, specific occupational therapy treatment sessions were planned one hour on daily basis for six weeks. Therapist initially at first to three weeks was focus on upper limb preparatory activities goals like muscle strengthening, endurance and passive full joint range of motion exercises in different position in order to maintain the joint optimal range of motion and to avoid the contracture (Figure 2). Later on gradually at four weeks patient muscle power and endurance level was improved and therapist was planned to start functional mobility training. Which included bed rolling, pelvic bridging, supine to sit, body weight transfer on both hand, trunk rotation, transfer from bed to chair, vice versa, sit to stand and reach out helps to perform activities of daily livings. Mean time patient was also got physiotherapy sessions and physical therapist was main focused on his ambulation and gait training. Slowly patient was able to walk with wide base gait on uneven surface. Occupational therapist specially instructed and guides the family to perform environmental modification such as safe access, shower stool, steps ramps and provide the assistive device like long handled aids, plat guard, and adaptive spoon in order to carry out easily grooming and feeding task at home. However at the fifth weeks of occupational therapy sessions therapist was planned to focus on deficit sensation goals and used compensatory techniques and sensory re-education therapy in order to normalize sensation. Further at week six occupational therapist was noted that patient motor transitional skill significantly was improved and now he was able to carry out upper limb active assisted gross movements and in activities of daily livings goals he was able to pick up and drink from a cup using both hands; bring food to his mouth with an adapted spoon. He initially needed plate guard and minimal assistance for placement the food because adducted thumbs and minimal active finger flexion and extension in both hand. He was also able to carry brush towards his teeth with the help of a universal cuff, although he required minimal assistance with shaving and minimal to moderate assistance with dressing the upper and lower extremities. Though occupational therapist was decided to recommend outrigger splint in order to improve passive range of motion in metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints of fingers. While in the area of sensation. It was noted that moderate protective sensation was improved and patient was able to recognize the deep nosiest stimulus and differentiate between hot & cold temperature. Sensation of numbness in both extremities was decreased and patient scored on modified Barthel index scale 86 out of 100. These changes was demonstrate that the occupational therapy treatment plan was well planned, and helpful in maintaining and achieving the maximum functional skills in GBS and minimize the chances of long term disability.
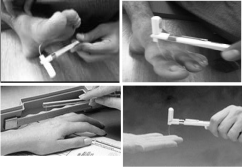
Figure 2:
Discussion
In GBS, it was seen that acute flaccid paralysis is a shocking situation [8]. In which patient loss all of his vocational abilities and considering himself as disable person. Occupational therapy rehabilitation can help the GBS patient to maintain and further stop his motor and sensory demyelination feature and regain his pervious lost functions. The comprehensive occupational therapy rehabilitation treatment was provided to GBS patient in this case study demonstrated considerable improvement in his motor, sensory and functional skills. However GBS is a very rare disease and there is scarcity of studies documenting the effect of occupational therapy in Rehabilitation of Guillain Barre Syndrome [9,10]. It is difficult to receive adequate sample size in rare conditions like GBS to conduct scientifically studies, so occupational therapists must always embark upon publishing their experiences so that some guidelines can draw to treat such disorders which would then serve as critical guide to parents and especially to occupational therapists who encounter such patients.
Conclusion
This case study showed that occupational therapy rehabilitation is effective for the management of abruptly loss of motor, sensory and vocational abilities of GBS patients. Our results of treatment techniques preparatory activities, range of motion exercise, functional training and sensory re-education therapy showed maximum improvement in upper extremities gross and fine motor work, functional abilities and some gain in sensation endorsed that occupational therapy
Rehabilitation services must be available to GBS patients and patients afflicted with similar condition can open up window of opportunity for them to prevent complication and gain anticipation that they are treatable to live independent.
References
- Khan F, Stevermuer T, Simmonds F. Rehabilitation for Guillain Barre Syndrome: Analysis of the Australian rehabilitation outcomes dataset. Journal of Clinical Medicine and Research. 2010; 2: 91-97.
- Orsini M, Freitas M, Presto B, Mello M, Reis C, Silveira v, et al. Guideline for neuromuscular rehabilitation in Guillain-Barré Syndrome: what can we do? Rev Neuroscience. 2010; 18: 572-580.
- Feasby T, Banwell B, Benstead T, Bril V, Brouwers M, Freedman M, et al. Guidelines on the use of intravenous immune globulin for neurologic conditions. Transfus Med Rev. 2007; 21: S57-107.
- Dhadke SV, Dhadke VN, Bangar SS, Korade MB. Clinical profile of Guillain Barre syndrome. J Assoc Physicians India. 2013; 61: 168-172.
- Alter M. The epidemiology of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1990; 27 Suppl: S7-12.
- Mays ML. Incorporating continuous passive motion in the rehabilitation of a patient with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Am J Occup Ther. 1990; 44: 750-754.
- Hansen M. Guillain-Barré syndrome, CIDP and Variants guideline for physical and occupational therapy. GBS/CIDP foundation International.
- Anis-ur-Rehman, Idris M, Elahi M, Jamshed, Arif A. Guillain Barre syndrome: the leading cause of acute flaccid paralysis in Hazara division. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2007; 19: 26-28.
- Khan F. Rehabilitation in Guillian Barre syndrome. Aust Fam Physician. 2004; 33: 1013-1017.
- Ohura T, Ishizaki T, Higashi T, Konishi K, Ishiguro R, Nakanishi K, et al. Reliability and validity of a performance evaluation tool based on the Modified Barthel Index. International Journal of Therapy and Rehabilitation. 2011; 18: 422-428.