
Special Article - Cancer Rehabilitation
Phys Med Rehabil Int. 2015;2(5): 1050.
Clinical Images in Medicine
Ying Guo¹* and Liat Goldman²
1Department of Palliative Care and Rehabilitation Medicine, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, 1515 Holcombe Boulevard, Houston, USA
2Department of Cardiology, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, 1515 Holcombe Boulevard, Houston, USA
*Corresponding author: Ying Guo, Department of Palliative Care and Rehabilitation Medicine, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, 1515 Holcombe Boulevard, Houston, TX 77030
Received: June 09, 2015; Accepted: June 09, 2015; Published: June 10, 2015
Clinical Image
A 70- year-old male with history diabetes mellitus, gout, hypertension, coronary heart disease (CHD) underwent coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) in April 2013. Post operatively patient was found to have pancytopenia, work-up led to the diagnosis of Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Patient underwent two cycles of chemotherapy, and presentedwith failure to thrive 7/30/13. Patient’s weight loss (Panel A) led to an investigation of his swallow. His modified barium swallow study on 8/1/13 showed that the patient had multiple episodes of penetration with the thin liquid barium at the level of the cords. He was insensate to this until the material started to fall below the vocal cords, then the patient did cough and cleared the material. Speech pathologist recommended tube feeding and nectar thick liquids for pleasure only. Sagittal view of neck during swallow study (Panel B) and subsequent CT of the neck (Panel C) showed large anterior cervical osteophytes compressing the posterior pharyngeal wall. He underwent percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy placement 8/13/13 and was ultimately discharged to home after acute rehabilitation stay. Anterior cervical osteophytes of this magnitude are quite rare and are sometimes associated with Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis [1] as in this case or Ankylosing Spondylitis [2].
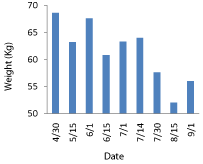
Panel A: Text Here.
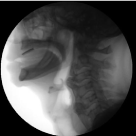
Panel B: Text Here.
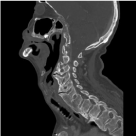
Panel C: Text Here.
References
- Proescholdt FF, Markart MM, Ertel WW. Postoperative radiotherapy in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: prophylaxis of recurrence after resection of osteophytes from C3 to C5 in a case of dysphagia. J Surg Case Rep. 2014; 2014.
- Albayrak I, Bağcacı S, Sallı A, Kucuksen S, Uğurlu H. A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis. Korean J Intern Med. 2013; 28: 614-618.