
Review Article
Austin J Pharmacol Ther. 2025; 12(3): 1195.
Pharmacopoeial Standards for Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies: Rituximab A Case Study
Kalaivani M*, Goyal A, Chaudhary P and Raghuvanshi RS
Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (Govt. of India), Ghaziabad, India
*Corresponding author: Kalaivani M, Senior Scientific Officer, Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Govt. of India, Sector-23, Raj Nagar, Ghaziabad-201 002, UP, India Email: kalaivani.ipc@gov.in
Received: April 11, 2025 Accepted: April 24, 2025 Published: April 28, 2025
Abstract
Globally, more than 160 therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) biosimilars are approved for marketing, including 58 in India market. The rapid growth of these therapies highlights the need for streamlined regulatory oversight and robust quality assurance to ensure their efficacy and safety. The quality of therapeutic mAbs, like all medicines, is maintained through pharmacopoeial standards and established quality control strategies. Pharmacopoeias are collections of legally required quality standards for drugs and excipients used in the manufacturing of approved drugs within a country, which must be adhered to by all who produce, distribute, or oversee these medicines. Currently, general guidance for these products is available in the United States Pharmacopoeia (USP), European Pharmacopoeia (Ph.Eur.) and Indian Pharmacopoeia (IP). However, specific pharmacopoeial monographs for mAbs are limited, for example Rituximab included in the Indian Pharmacopoeia 2022 and Infliximab concentrated solution in the Ph.Eur. in 2019 (Supplement 9.6). This article discusses the challenges and opportunities in establishing quality standards for therapeutic mAbs, using the IP 2022 monograph on Rituximab as a case example. The authors also propose a harmonized approach or collaboration among leading pharmacopoeias to develop monographs for these essential therapeutics.
Keywords: Rituximab; Pharmacopoeial specifications; Monoclonal antibody; Regulatory; Biotherapeutics; Quality standards
Introduction
Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have emerged as a crucial class within high-molecular-weight biopharmaceuticals, demonstrating remarkable therapeutic potential. Generally, mAbs are immunoglobulin molecules derived from a single B-cell clone, produced using recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology and hybridoma technology [1-4]. Solid tumours, haematologic malignancies, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, and ankylosing spondylitis are few of the chronic and life-threatening diseases for which these mAbs have revolutionised therapy strategies [5-9]. Over the last three decades, over 160 therapeutic mAbs have gained approval as treatments from leading regulatory bodies, including the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization, CDSCO; European Medicines Agency, EMA and U.S. Food and Drug Administration, FDA [10-14].
Developing quality standards for therapeutic mAbs, which are biologically derived and structurally complex, demands specialized attention, along with sophisticated testing and controls to ensure their identity, purity, and potency. The World Health Organization (WHO) has provided foundational guidance through its Technical Report Series 822, 1992: Annex 3 [15]. Additionally, manufacturers are advised to consult other National and International guidelines which include both physicochemical and biological characterization of recombinant mAbs [16-18]. These guidelines emphasize the need to assess Critical Quality Attributes (CQA) and Key Quality Attributes (KQA) using advanced, high-resolution analytical techniques capable of detecting subtle variations in the product. The use of these techniques is crucial for maintaining product consistency and detecting any structural or functional changes.
In the present article, the authors explore the process of developing pharmacopoeial quality standards for therapeutic mAbs illustrating the approach using Rituximab as a case study for adopting these standards in an official monograph.
Regulatory and Pharmacopoeial Aspects of Therapeutic Mabs: Worldwide
Drug regulatory agencies and the WHO provide comprehensive guidelines for the approval of mAbs as drugs and biosimilars (Table 1) [17,19]. Additionally, the WHO offers specific guidelines for the nomenclature of therapeutic mAbs [20]. The therapeutic mAbs market is expected to increase at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.30% from its 2020 valuation of about $125 billion to $494.53 billion by 2030 [20-21]. The success of therapeutic mAbs and the expiration of patents have driven the development of biosimilar therapeutics. Currently, more than 160 therapeutic mAbs have been approved for marketing worldwide [23]. Table 2 lists the therapeutic mAbs approved in the US, EU, and India. Drug regulatory authorities, including the US-FDA, EMA, CDSCO and WHO, have established comprehensive guidelines for granting marketing authorization for these products, either as innovator drugs or biosimilars (Table 1). The rapid market expansion of these molecules highlights the critical need for robust quality assurance to ensure their efficacy and safety. Pharmacopoeias play a crucial role in improving patient access to high-quality drugs, minimizing adverse effects caused by substandard medicines, and promoting consistency in drug pricing through quality assurance [24-26]. These standards, available as public compliance documents, enable independent quality verification of a product throughout its shelf life [27]. International pharmacopoeia serves as a mandatory public standard and provides an authoritative framework for assessing the identity, strength, and purity of therapeutics [28]. Additionally, it facilitates the incorporation of harmonized testing methods as quality standards, ensuring safety and quality of medicines. The Indian Pharmacopoeia (IP) serves as the official reference for drug and pharmaceutical standards, including biopharmaceuticals approved for in India. These standards are in accordance with the provisions of the "Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940, and Rules" framed under it. Notably, the current edition of IP 2022 includes monographs for rituximab and rituximab injection [29-30]. The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) has also played a key role in establishing quality standards for biologics, contributing to its growing collection of monographs and general chapters for drugs marketed in the United States. In 2012, USP initiated efforts to outline a well-defined set of quality requirements for recombinant therapeutic mAbs. This led to the introduction of the official General Chapter <129>, titled "Analytical Procedures for Recombinant Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies" [31].
S.No
Pharmacovigilance
USA (US-FDA)
EU (GaBi online)
India (CDSCO)
1
Regulatory authority
United States Food and Drugs Administration
European Medicines Agency
Central Drugs Standards Control Organization
2
Regulatory pathways
No different pathways and/or data requirements for imported drugs vs. locally manufactured drugs
Different pathways and/or data requirements for imported drugs vs. locally manufactured drugs
4
Biosimilar Guideline-Year of Publication
2010
2005
2012
5
Nomenclature
Biological qualifier scheme
No biological qualifier scheme
7
Applicable Guidelines
Scientific considerations in demonstrating bio-similarity to a reference product
- Guideline on Similar biological medicinal products
- Guideline on Similar biological medicinal products containing biotechnology-derived proteins as active substance: non-clinical and clinical issues
- Similar biological medicinal products containing biotechnology-derived proteins as active substance: quality issues along with product-specific guidelines
- CDSCOguidanceforindustry,2008
- Submission of Clinical Trial Application for Evaluating Safety and Efficacy
- Requirement for permission of New Drug Approval
- Post approval changes in Biological products: Quality, Safety and Efficacy Documents
- Preparation of Quality Information for Drug Submission for New Drug Approval: Biotechnological/Biological Products
- Guidelines on Similar Biologics: Regulatory Requirements for Marketing authorization in India 2016.
8
Number of mAbs Biosimilars approved
26
37
No approval as Biosimilar but 58 rDNA based drugs are approved as ‘New Drugs’
Table 1: Regulatory guidelines for marketing authorization of therapeutic mAbs in US, EU and India.
Europe (EMA)
India (CDCSO)
Biosimilar
Year of approval
Manufacturer
Biosimilar
(Brand name)Year of approval
Manufacturer
Therapeutic mAb
Year of approval
Manufacturer/
ImportersAdalimumab Biosimilar
Adalimumab-adaz
2018
Sandoz Inc
Hyrimoz
2018
Sandoz GmbH
Adalimumab
2017
Hetero Drugs
LimitedHefiya
Halimatoz
Hulio
(adalimumab-fkjp)2020
Sandoz Inc
Imraldi
2017
Samsung Bioepis UK Limited (SBUK)
2015
Reliance Life Sciences Private Limited
Idacio (adalimumab-aacf)
2022
Fresenius Kabi USA
Amgevita
2017
Amgen Europe B.V.
2014
Cadila Healthcare Limited
Yusimry (adalimumab-aqvh)
2021
CoherusBioSciences, Inc.
Solymbic
2017
Abrilada
(adalimumab-afzb)2019
Pfizer Inc.
Cyltezo
2017
BoehringerIngelheim International GmbH
Hadlima
(adalimumab-bwwd)2019
Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd.,
Hulio
2018
Viatris Limited
Adalimumab-adbm
2017
BoehringerIngelheim
Pharmaceuticals,IncIdacio
2019
Fresenius Kabi Deutschland GmbH
Kromeya
2019
Amsparity
2020
Pfizer Europe MA EEIG
Adalimumab -atto
2016
Amgen Inc.,
Yuflyma
2021
Celltrion Healthcare Hungary Kft.
Hukyndra
2021
StadaArzneimittel AG
Libmyris
2021
Infliximab Biosimilar
Inflectra
(Infliximab-dyyb)2016
Celltrion, Inc.
Flixabi
2016
Samsung Bioepis UK Limited (SBUK)
Infliximab
2014
Reliance Life Sciences
Avsola
(infliximab-axxq)2019
-
-
-
-
2019
M/s Biocad India Pvt.
LtdInfliximab-abda
2017
Samsung Bioepsis Co., Ltd.,
Remsima
2013
Celltrion Healthcare Hungary Kft.
2013
M/s Johnson & Johnson Limited
importIxifi (Infliximab-qbtx)
2017
Pfizer Inc,
Inflectra
2013
Pfizer Europe MA EEIG
Zessly
2018
Sandoz GmbH
Trastuzumab Biosimilar
Trastuzumab-dkst
2017
Mylan GmbH
Herzuma
2018
Celltrion Healthcare Hungary Kft.
Trastuzumab
2002
Roche Scientific
Zercepac
2021
Accord Healthcare S.L.U.
2018
Intas Pharmaceuticals Limited
Kanjinti
2018
Amgen Europe B.V., Breda
2015
Reliance Life Sciences Private Limited
Trazimera
2018
Pfizer Europe MA EEIG
2015
Cadila Healthcare Private Limited
Ogivri
2018
Viatris Limited
2018
Dr Reddy Laboratories Ltd
Herzuma
(trastuzumab-pkrb)2018
CELLTRION, Inc.
-
-
2013
Biocon Ltd
Kanjinti
(trastuzumab-anns)2019
Amgen Inc.
-
2002
Taksal pharma Private Limited
Trazimera
(trastuzumab-qyyp)2019
Pfizer Ireland Pharmaceuticals
-
-
-
2018
Biocad India Pvt Ltd
Ontruzant
(trastuzumab-dttb)2019
CELLTRION, Inc.
-
-
-
2018
Vardhman Health
SpecialitisPvt LtdBevacizumab Biosimilar
Bevacizumab-awwb
2017
Amgen Inc.
Mvasi
2018
Amgen Europe B.V.
Bevacizumab
Roche Limited
2016
Hetero Drugs Limited
2016
Intas Pharmaceuticals Limited
Vegzelma (bevacizumab-adcd)
2022
Celltrion, Inc.
Alymsys
2021
Mabxience Research SL
2016
Reliance Life Sciences Private Limited
Alymsys (bevacizumab-maly)
2022
Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC
Aybintio
2020
Samsung Bioepis NL B.V.
-
2017
Biocon Ltd.
Onbevzi
2021
Zirabev
(bevacizumab-bvzr)2019
Pfizer Inc.
Abevmy
2021
Mylan IRE Healthcare Limited
-
2017
Cadila Healthcare
Vegzelma
2022
Celltrion Healthcare Hungary Kft.
-
2018
Dr Reddy Laboratories Ltd
Zirabev
2019
Pfizer Europe MA EEIG
-
-
-
Oyavas
2021
STADA Arzneimittel AG
-
-
-
Equidacent
2020
Centus Biotherapeutics Europe Limited
-
-
-
Rituximab Biosimilar
Riabni
(rituximab-arrx)
2020
Amgen, Inc.
Truxima
2017
Celltrion Healthcare Hungary Kft.
Rituximab
2015
Hetero Drugs Limited
Blitzima
2017
Ruxience
(rituximab-pvvr)2019
Pfizer Ireland Pharmaceuticals Cork,
Riximyo
2017
Sandoz GmbH
2015
Reliance Life Sciences
2013
Zenotech Laboratories
Truxima
(rituximab-abbs)2018
CELLTRION, Inc.
Ruxience
2020
Pfizer Europe MA EEIG
2013
Intas Biopharmaceuticals
2012
Taksal Limited
2002
Roche Scientific Limited
2017
Biocad India Pvt Ltd
2018
Vardhman Health SpecialitisPvt Ltd
Secukinumab Biosimilar
Secukinumab
2015
Novartis Limited
2015
Sandoz Limited
Canakinumab
Canakinumab
2011
Novartis India Pvt Limited
Natalizumab
Natalizumab
2018
Eisai Pharmaceuticals India Pvt Ltd
Siltuximab
Siltuximab
2016
Johnson & Johnson Limited
Ofatumumab
Ofatumumab
2016
Novartis Healthcare Private Limited
Pembrolizumab
Pembrolizumab
2016
MSD pharmaceuticals Private Limited
Tocilizumab
Tocilizumab
2009
Taksal Limited
2018
Roche Scientific Limited
Denosumab
Denosumab
2018
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
2017
Dr Reddy Laboratories Ltd
Panitumumab
Panitumumab
2017
Dr Reddy Laboratories Ltd
Daclizumab
Daclizumab
2002
Roche Scientific Co
Nimotuzumab
Nimotuzumab
2013
Biocon Limited
Ranibizumab
Cimerli (ranibizumab-eqrn)
2022
CoherusBioSciences, Inc.
Byooviz2021
Samsung Bioepis NL B.V.
Ranibizumab
2007
Novartis (I) Limited
Byooviz
(ranibizumab-nuna)2021
Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd.
Ximluci
2022
STADA Arzneimittel AG
2019
M/s Sandoz Private Limited
Ranivisio
2022
Midas Pharma GmbH
2013
Intas Biopharmaceuticals
2014
Alcon Laboratories (India)
Pvt. Ltd.Omalizumab
Omalizumab
2015
Novo Nordisk India Pvt
Ltd2016
M/s Sandoz Private Limited
Table 2: Therapeutic mAbs and its Biosimilars approved by US-FDA, EMA and CDSCO.
The European Pharmacopoeia (Ph.Eur.) has achieved important milestone in the field of biopharmaceuticals with adoption of the monograph for Infliximab concentrated solution in European Pharmacopoeia in Ph. Eur. 9th edition, year 2019 [32-33].
Pharmacopoeial Standards as an Quality Control of Therapeutic Mabs: Rituximab a Case Study
Globally, pharmacopoeial standards for therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are established through two primary approaches: 1) General Chapters/Monograph provide overarching guidelines and test methods applicable to a broad range of mAbs. 2) Specific Monographs provide tailored guidance for individual mAb products, outlining specific tests and acceptance criteria based on their unique characteristics [30]. Table 3 and 4 illustrate the availability of pharmacopoeial standards for therapeutic mAbs in various pharmacopoeias, including IP, USP, Ph.Eur., and the Int Pharm. Table 3 mainly focuses on general requirements, while Table 4 presents specific monographs for individual mAb products.
Standard’s Name
Pharmacopoeial status
Indian Pharmacopoeia [IP, 2022]
US Pharmacopoeia [USP, 2024]
European Pharmacopoeia [Ph.Eur. 11.2]
British Pharmacopoeia [BP, 2022]
WHO/International Pharmacopoeia
[WHO, 2022]General requirements/Guidelines
Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies for human use
<129>
Analytical Procedures For Recombinant Therapeutic Monoclonal AntibodiesMonoclonal Antibodies For Human Use
Monoclonal Antibodies For Human Use
3.1.1 Guidelines on evaluation of monoclonal antibodies as similar biotherapeutic products (SBPs)
Monographs
Rituximab
Not Available
Infliximab conc. solution
Infliximab conc. solution
Not Available
Rituximab injection
Ref. standard
NA
Monoclonal IgG System Suitability
Infliximab BRP
Not available
Infliximab
Monoclonal IgG1, mAb001
Adalimumab
Monoclonal IgG1, mAb002
Bevacizumab
Monoclonal IgG1, mAb003
Infliximab CRS
Trastuzumab
Cetuximab
Trastuzumab
Table 3: Pharmacopoeial monograph and standards for therapeutic mAbs available in various pharmacopoeias.
S.No
Pharmacopoeia requirements/ Specifications/Monograph content
Pharmacopoeial Specification
Rituximab (Drug Substance),(IP, 2022)
Rituximab injection (Drug Product), (IP, 2022)
Infliximab concentrated solution (Drug Substance), (Ph. Eur. 11.2)
1
Host-cell-derived proteins
NMT 100 ppm
-
Limit as approved by the competent authority
2
Host-cell- and vector-derived DNA
NMT 10 ng per dose
-
3
Category
Anticancer
Anticancer
Monoclonal antibody (TNF alfa)
4
Description
Clear colorless to pale yellow liquid free from particles that can be observed by visual observation.
Clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow liquid.
Opalescent or slightly opalescent, colorless or light yellow liquid.
5
Identification
Determine by method B and any two methods from method A,C, D, E
Determine by method A, B or D and C
-
5.A
Bioassay
Complies with the biological activity as described in assay
It complies with the limits of the assay (potency)
5.B
Method
Peptide mapping by HPLC
Capillary zone electrophoresis
Peptide mapping by HPLC
Specification
The retention time of established marker peaks should be within ± 0.7 minutes of the reference solution marker peaks
Positive identity is confirmed if the difference in migration time between the main peak of the reference solution and test solution is equal or less than 0.1 minute
-the profile of the chromatogram obtained with the test solution corresponds to that of the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution;
-no additional peak in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution has an area greater than 0.5 per cent of the sum of the areas of peaks 1 to 205.C
Sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
The principal band in the electropherogram obtained with test solution is similar in position and intensity to the principal band in the electropherogram obtained with reference solution.
-
5.D
Method
Capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE)
Iso Electric Focusing using capillary electrophoresis (IEF-CE)
-
Specification
Positive identity is confirmed if the difference in migration time between the main peak of the reference solution and test solution is less than or equal to 0.1 min.
pI of principal band in reference solution is 9.3±0.2. In the electropherogram obtained with the test solution, no band other than the principal band is more intense than the principal band in the electropherogram obtained with reference solution.
5.E
IEF-CE
In the electropherogram obtained with reference solution, the pI of principal is 9.3 ± 0.2. In the electropherogram obtained with test solution no band other than the principal band is more intense than the principal band in the electropherogram obtained with reference solution.
NA
-
6
Tests
6.1
pH
6.3 to 6.7
As approved by the competent authority
6.2
Osmolality
NA
Not less than 250mosmol per kg
NA
6.3
Impurities with molecular masses differing from that of Rituximab
Method 1
Capillary Electrophoresis under reducing and non-reducing conditions
Size-exclusion chromatography
Specification
The corrected percentage area low molecular weight impurities are not more than 10.0 per cent.
Under reducing conditions: The corrected percentage area of non-glycosylated heavy chain is Not more than 2.0 per cent
Under non-reducing conditions: The corrected percentage area low molecular weight impurities is not more than 10.0 per centsum of all peaks other than the monomer peak: maximum 2 per cent
Method 2
Sodium dodecyl-sulfatepolyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
-
Specification
The band(s) observed in the test solution and reference solution match in position and intensity on visual observation.
6.4
Related substances/related proteins
Method
Size exclusion chromatography
Capillary electrophoresis (2.2.47) under both reducing and non-reducing conditions
Specification
Complies with the limits approved for the particular product
The sum of the peaks with retention times less than that of the principal peak is NMT 2.0 per cent, the sum of the peaks with retention times higher than that of the principal peak is NMT 7.0 per cent and the sum of the peaks with retention times lesser and higher than that of the principal peak is not more than 9.0 per cent.
Reducing conditions:
– sum of all peaks other than heavy chain and light chain: maximum 2 per cent, unless otherwise justified and authorised;
Non-reducing conditions:
– sum of all peaks other than the principal peak: maximum 8 per cent.6.5
Charged variants
Method
Ion-exchange liquid chromatography
Isoelectric focusing (2.2.54): use suitable agarose gels
Specification
Acidic variants = 45 %
Main peak = 35%– Electropherogram obtained with the test solution is similar to the electropherogram obtained with reference solution (b) and no additional bands obtained with test solution. Isoelectric points of the principal components of the test solution and reference solution (b) do not differ by more than 0.05 pI units;
6.6
Glycan distribution
Method
Capillary electrophoresis with fluorescence detection
Any suitable method as per general chapter ‘Glycan analysis of glycoproteins’
Specification
The corrected area percentage of each glycan should comply with the limits approved by National Regulatory Authority (NRA).
The percent area of the peaks corresponding to galactosylated glycan should be between 35 and 65 per cent.The corrected area percentage of each glycan should comply with the limits approved by National Regulatory Authority (NRA).The percent area of the peaks corresponding to galactosylated glycan should be between 35 and 65 per cent.
percentage of fucosylatedglycans: as authorized by the competent authority;
percentage of afucosylatedglycans: as authorized by the competent authority;
percentage of sialylatedglycans: as authorized by the competent authority.6.7
Bacterial endotoxins
NMT 1.0 EU per mg or equivalent to EU per ml
NMT 1.0 EU per mg
NA
6.8
Protein A leachetes
Comply with the limits as approved by NRA
-
As approved by the competent authority
6.8
Tests stated under Parenteral
PreparationsNA
Complies
NA
Residual Protein A
NA
NA
Suitable immunochemical method based on an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Limit: As approved by the competent authority
6.9
Protein
Method
Ultraviolet/visible spectrophotometry
Specification
Not less than 90 per cent and Not more than 110 per cent of the stated amount of protein.
NA
7
Assay
PotencyMethod
Complement dependent cytotoxicity assay by using WIL2-S cells
Suitable cell-based assay based on the inhibitory action of infliximab on the biological activity of TNF-a
Specification
Rituximab contains not less than 80 per cent and not more than 125 per cent of the stated potency
The estimated potency is not less than 80 per cent and not more than 120 per cent relative to the reference solution.
8
Storage
Store at temperature as approved by NRA.
Store at 2 to 8° in an airtight container.
In an airtight container, under approved conditions
9
Labeling
NA
The label states (1) Content of rituximab in mg per ml (2) name of product with generic name (3) drug product (injection) in mg per ml (4) Potency; (4) storage temperature.
The label states the content in milligrams of protein per millilitre.
Table 4: Summary of pharmacopoeial specifications of Rituximab Monographs (IP, 2022) and Infliximab concentrated solution (Ph.Eur. 11.2.).
General Guideline/General Chapter for Therapeutic Mabs
The IP provides comprehensive guidance on the development and manufacturing of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) [29]. This guidance specifically focuses on mAbs intended for therapeutic use, excluding those used as reagents in other drug manufacturing processes, for in vivo diagnostics, or for prophylactic purposes. The guidance encompasses key aspects such as general principles for mAb development, product development including cloning and cell line development, process development, analytical method development, process characterization, and analytical characterization, nonclinical and clinical studies required for mAb development, and manufacturing considerations such as large-scale manufacturing processes, process validation, lot release testing, establishment and use of reference standards, shelf-life determination, and considerations for storage and stability. Furthermore, the IP recommends adhering to the "International Nonproprietary Names (INN) for monoclonal antibodies" guidelines issued by the World Health Organization for consistent and standardized nomenclature of mAbs [20]. Figure 1 provides a brief overview of the general steps involved in the development of therapeutic mAbs.
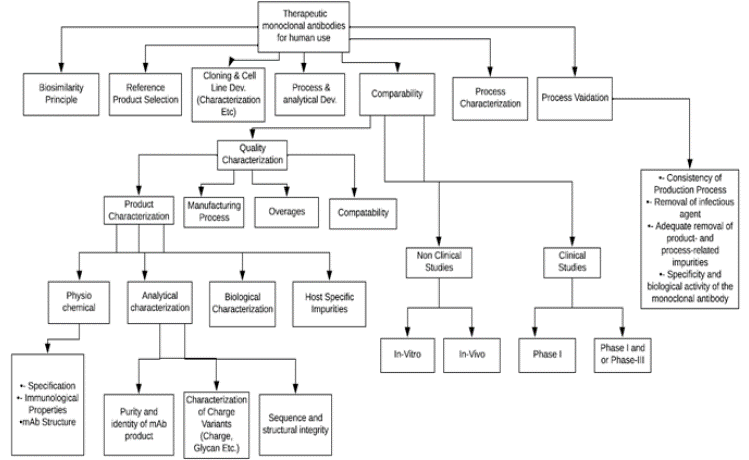
Figure 1: A brief overview of general steps in monoclonal antibody development.
Specific Pharmacopoeial Monograph for Therapeutic Mabs
Globally only two pharmacopoeias provide the quality standards of specific monoclonal antibodies despite more than 160 monoclonal antibodies approval. The IP 2022 edition has introduced specific monographs for Rituximab (Drug Substance) and Rituximab injection (Drug Product). These monographs outline quality standards for rituximab encompassing physicochemical, biological, and microbiological attributes to ensure acceptable quality of both the drug substance and the drug product. General tests include assessments of appearance, extractable volume, osmolality, pH, protein content, solubility, sub-visible particulate matter and water content as appropriate. Identification tests include biological activity, peptide mapping, capillary zone electrophoresis, and isoelectric focusing. Purity assessments encompass analysis of impurities with molecular masses differing from Rituximab (using techniques like CE-SDS and SDS-PAGE), related substances (using Size Exclusion Chromatography), charged variants (using Ion Exchange Chromatography), glycan distribution (using capillary electrophoresis with fluorescence detection), and bacterial endotoxins. Other tests include IgG-isotyping and protein content determination. Potency is determined by complement-dependent cytotoxicity assays using suitable cell lines. The potency limits are established and approved during the marketing authorization process [30].
Challenges in Establishing Pharmacopoeial Standards for Rituximab
Therapeutic mAbs exhibit inherent structural complexity and intrinsic heterogeneity. Notably, the Indian market boasts over 18 marketed authorizations for Rituximab, reflecting its biosimilarity to the innovator product based on comparable protein structure and function [34-35]. The development of Rituximab drug substance and drug product monographs for the IP involved extensive input and data from domestic manufacturers and importers.
A significant challenge arose from the observed diversity in quality parameters, particularly in terms of molecular size, charge, and glycosylation patterns, among products from different manufacturers/ importers. Studies have consistently highlighted these variations [36-44]. This heterogeneity presented a considerable challenge in establishing a single, universally applicable monograph for Rituximab. However, to address this complexity, the IP monograph development process incorporated flexibility in several key areas.
Furthermore, the monograph provides flexibility in the use of alternative pharmacopoeial standards [45,46]. Acceptance criteria were defined as ranges based on approved specifications. The most suitable methods and specifications were finalized through a rigorous process involving collaboration with the National Institute of Biologicals, Noida. This collaborative effort, coupled with the robust IP monograph development process, ultimately led to the successful finalization of the Rituximab drug substance and injection monographs.
Conclusion
Pharmacopoeial specifications are indispensable for ensuring the quality control and assurance of therapeutic mAbs. Compliance with these specifications is mandatory for manufacturers, national control laboratories, and drug regulatory authorities. Pharmacopoeial monographs provide robust analytical methods and their acceptance criteria for assessing the identity, purity, and potency of therapeutic mAbs. They also play a crucial role in identifying products that do not meet established quality standards (Not suitable quality, NSQ samples). The valuable knowledge gained from developing specific monographs for Rituximab and the "General requirements for therapeutic mAbs" within the IP will undoubtedly contribute to the development of robust pharmacopoeial standards for other therapeutic mAbs. Adherence to these standards will ensure the consistent quality, safety, and efficacy of therapeutic mAbs.
Despite the challenges encountered in developing and implementing these standards, it is crucial to recognize the immense therapeutic potential of mAbs, including biosimilars, in treating lifethreatening diseases and improving global healthcare outcomes. By addressing these challenges and continuing to refine pharmacopoeial standards, we can ensure that patients worldwide have access to safe and effective mAb therapies.
Acknowledgement
Authors acknowledge the technical support provided by IPC’s Expert Working Group-Biological and rDNA products, National Institute of Biologicals, Noida, India and Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC), Ghaziabad, India.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the conceptualization and development of the manuscript through collaborative meetings. AG and PC drafted the manuscript while MK critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors reviewed and provided substantial and comprehensive feedback on each draft of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
References
- Mitra S and Tomar PC. Hybridoma technology; advancements, clinical significance, and future aspects. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2021; 19: 159.
- Köhler G and Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975; 256: 495-497.
- Cabilly S, Riggs AD, Pande H, Shively JE, Holmes WE, Rey M, et al. Generation of antibody activity from immunoglobulin polypeptide chains produced in Escherichia coli. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 1984; 81: 3273-3277.
- Holler PD, and Chik JK. Hybridoma Production. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. 2009; 86: 11.4.1-11.4.29.
- Reichert JM, Rosensweig CJ, Faden LB, Dewitz MC. Monoclonal antibody successes in the clinic. Nat Biotechnol. 2005; 23: 1073-1078.
- Sliwkowski MX, Mellman I. Antibody therapeutics in cancer. Science. 2013; 341: 1192-1198.
- Chan AC, Carter PJ. Therapeutic antibodies for autoimmunity and inflammation. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2010; 10: 301-316.
- Scott LJ. Infliximab: a review in Crohn’s disease. Drugs. 2016; 76: 1347-1357.
- Nash P, Vanhoof J, Hall S, Arulmani U, Tarzynski-Potempa R, Unnebrink K, et al. Randomized Crossover Comparison of Injection Site Pain with 40 mg/0.4 or 0.8 mL Formulations of Methotrexate. Clinical Therapeutics. 2018; 40: 428- 439.
- Becker M, Schneider CK, Ebel B. ‘Omics’, biomarker discovery, and FDA’s critical path. New England Journal of Medicine. 2006; 355: 2255-2257.
- Hofmann F. The European regulatory environment for biosimilars. Generics and Biosimilars Initiative Journal (GaBI Journal). 2013; 2: 189-193.
- Snodin DJ, McCrossen SD. Guidelines and pharmacopoeial standards for pharmaceutical impurities: overview and critical assessment. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012; 63: 298-312.
- Keitel S. Inside EDQM: the role of the pharmacopeia in a globalized world. Pharm Technol. 2010; 34.
- Niazi SK. Biosimilars: Harmonizing the Approval Guidelines. Biologics. 2022; 2: 171–195.
- WHO good manufacturing practices for biological products. Annex 3. Replacement1 of Annex 1 of WHO Technical Report Series, No. 822.
- Guidelines on Similar Biologics. Regulatory Requirements for Marketing Authorization in India. 2016.
- World Health Organization. Guidelines on evaluation of biosimilars, Annex 2 of WHO Technical Report Series, No. 977. 2022: 1-52.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Guideline on development, production, characterization and specification for monoclonal antibodies and related products. EMA/CHMP/BWP/532517/2008; 1-13.
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for national authorities on quality assurance for biological products. 1992 Annex 2, WHO Technical Report Series No. 822.
- World Health Organization. New INN monoclonal antibody (mAb) nomenclature scheme, INN Working Doc. 21.531. 2021: 1-3.
- Ecker DM, Jones SD, Levine HL. The therapeutic monoclonal antibody market. MAbs. 2015; 7: 9-14.
- Kaplon H, Chenoweth A, Crescioli S, et al. Antibodies to watch in 2022. MAbs. 2022; 14: 2014296.
- Lyu X, Zhao Q, Hui J, Wang T, Lin M, Wang K, et al. The global landscape of approved antibody therapies, Antibody Therapeutics. 2022; 5: 233–257.
- Belz S. Das Arzneibuch. EinwichtigerPfeiler der Arzneimittelsicherheit [The pharmacopoeia. An important pillar of drug safety]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2006; 49: 1205-1211.
- Soldi A. Pharmacopoeia as quality codex for the manufacturers. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 1975; 11: 269-280.
- Grainger HS. The role of the pharmacopoeia in the control of pharmaceutical preparations. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 1975; 11: 305-313.
- World Health Organization. WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations. Annex 1 Good pharmacopoeial Practices. WHO Technical Report Series No. 996, 2016.
- The International Pharmacopoeia, 6th ed. [internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016.
- Indian Pharmacopoeia. General Requirements. Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies for Human Use, IP. 2022; 3: 4576-4582.
- Indian Pharmacopoeia. Rituximab Drug substance and Rituximab injection monographs, IP. 2022; 3: 4669-4682.
- The United States Pharmacopeia. General Chapters <129> Analytical Procedures for Recombinant Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies, 2022.
- European Pharmacopoeia. Ninth ed. Monoclonal Antibodies For Human Use. European Pharmacopoeia. 2019; 10: 8.
- European Pharmacopoeia. Tenth ed. Infliximab Concentrated Solution. European Pharmacopoeia. 2024; 11: 2.
- Kaur T, Shukla BN, Yadav VK, Kulkarni MJ, Rao A. Comparison of glycoprofiles of rituximab versions licensed for sale in India and an analytical approach for quality assessment. J Proteomics. 2021; 244: 104267.
- Duivelshof BL, Jiskoot W, Beck A, Veuthey JL, Guillarme D, D’Atri V. Glycosylation of biosimilars: Recent advances in analytical characterization and clinical implications. Anal Chim Acta. 2019; 1089: 1-18.
- Sran KS, Sharma Y, Kaur T, Rao A. Post-translational modifications and glycoprofiling of palivizumab by UHPLC-RPLC/HILIC and mass spectrometry. J Proteins Proteom. 2022; 13: 95-108.
- Edwards E, Livanos M, Krueger A, Dell A, Haslam SM, Mark Smales C, et al. Strategies to control therapeutic antibody glycosylation during bioprocessing: Synthesis and separation. BiotechnolBioeng. 2022; 119: 1343-1358.
- Segu Z, Stone T, Berdugo C, Roberts A, Doud E, Li Y. A rapid method for relative quantification of N-glycans from a therapeutic monoclonal antibody during trastuzumab biosimilar development. mAbs. 2020; 12: 1750794.
- Tiwold EK, Gyorgypal A, Chundawat SPS. Recent advances in biologic therapeutic N-glycan preparation techniques and analytical methods for facilitating biomanufacturing automation. J Pharm Sci. 2023; 112: 1485-1491.
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P, et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th edition. New York: Garland Science; 2002. Analyzing Protein Structure and Function.
- Aich U, Lakbub J, Liu A. State-of-the-art technologies for rapid and highthroughput sample preparation and analysis of N-glycans from antibodies. Electrophoresis. 2016; 37: 1468-1488.
- Aich U, Liu A, Lakbub J, Mozdzanowski J, Byrne M, Shah N, et al. An Integrated Solution-Based Rapid Sample Preparation Procedure for the Analysis of N-Glycans From Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies. J Pharm Sci. 2016; 105: 1221-1232.
- Yang X, Kim SM, Ruzanski R, Chen Y, Moses S, Ling WL, et al. Ultrafast and high-throughput N-glycan analysis for monoclonal antibodies. mAbs. 2016; 8: 706-717.
- Prior S, Hufton SE, Fox B, Dougall T, Rigsby P, Bristow A. Participants of the study. International standards for monoclonal antibodies to support pre- and post-marketing product consistency: Evaluation of a candidate international standard for the bioactivities of rituximab. MAbs. 2018; 10: 129-142.
- Zheng K, Bantog C, Bayer R. The impact of glycosylation on monoclonal antibody conformation and stability. mAbs. 2011; 3: 568-576.
- Batra J and Rathore A. Glycosylation of Monoclonal Antibody Products: Current Status and Future Prospects. Biotechnology progress. 2016; 32.