
Rapid Communication
Int J Nutr Sci. 2023; 8(2): 1078.
Association of Vitamin D and Endothelial Function in a Subsample of the Participants in the Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-BRASIL)
Sousa MCR¹; Silva IFO¹*; Reis EA²; Ribeiro ALP³; Brant LCC³; Gonçalves LG³; Barreto S³
¹Faculdade de Farmácia, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Brazil
²Departamento de Estatística, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Brazil
³Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Brazil
*Corresponding author: Silva IFO Faculdade de Farmácia, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais. Avenida Antônio Carlos, 6627 - Campus Pampulha Belo Horizonte - Minas Gerais - 31270-901, Brazil. Tel: +55 (31) 3409-6881, +55 (31) 99281-4057; Fax: +55 (31) 31 3409-6895 Email: iedafos@farmacia.ufmg.br or iedafos@yahoo.com.br
Received: September 15, 2023 Accepted: October 07, 2023 Published: October 14, 2023
Abstract
The Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-BRASIL) is a multicentric and multidisciplinary cohort study aimed at investigating the incidence and risk factors of chronic diseases. Vitamin D deficiency has been associated with several comorbidities. In this context, the need to assess the impact of vitamin D on endothelial dysfunction in a large-scale study is justified. Thus, in this study, serum levels of vitamin D were determined by HPLC in 509 participants of the ELSA-BRASIL, and its association with endothelial function parameters by Peripheral Arterial Tonometry (BPA and PATratio). Reduced levels of vitamin D were shown to be associated with indicative measures of worse endothelial function. In the logistic regression model, the variables male sex, white color, increase in age, BMI, triglycerides, and vitamin D<30ng/mL were also indicative of worse endothelial function. In summary, vitamin D has presented an association with endothelial function, which may indicate a protective action of vitamin D to the vascular endothelium.
Keywords: ELSA-BRASIL; Vitamin D; Endothelial dysfunction; EndoPAT
Introduction
Vitamin D is involved in cell development and growth, autoimmunity, insulin resistance and cardiovascular diseases [1,2]. Vitamin D levels are also possibly associated with endothelial function through the renin-angiotensin system, by promoting Nitric Oxide (NO) availability and immunomodulation [3,4].
There are indications that vitamin D could be somehow related to endothelial function, nonetheless the data found in the literature is contradictory [5,6] and inconclusive [7]. Hence the present study aimed to evaluate vitamin D and endothelial function in a subsample of adults residing in Minas Gerais participating in the Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-BRASIL) who underwent measurement of microvascular endothelial function by Peripheral Arterial Tonometry (PAT).
Materials and Methods
Overview
The present study is part of the ELSA-BRASIL, a multicentric cohort, approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG) under registration number ETIC 186/06. The project was carried out in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki.
A serum subsample of 509 participants, age 35 to 74 years old, was used to determine vitamin D levels. The endothelial function parameters were provided via a database collected between 2008 and 2010 by the researchers of the ELSA-BRASIL study, following standardized protocols. After quality control, the results of 20 participants were excluded due to technical issues.
Vitamin D blood concentrations were categorized into vitamin D levels above or below 30 ng/mL in accordance with the International Osteoporosis Foundation and the American Geriatrics Society, which designate vitamin D “insufficiency” when blood vitamin D is between 12 and 30 ng/mL [8,9].
Vitamin D Blood Analysis
Vitamin D blood concentration of the participants was quantified using the technique of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) according to [10].
Endothelial Function Assessment
The endothelial function was assessed using an automated device (EndoPAT2000; Itamar Medical, Caesarea, Israel). From these measurements, the PATratio was calculated, which is the ratio between the amplitude of the vascular pulse 90 to 120 seconds after cuff deflation and the mean basal pulse amplitude (mean BPA) [11,12].
Statistical Analysis
Categorical data were described by the absolute and relative frequencies, while continuous variables were summarized by the median and interquartile range (Q1-Q3).
To investigate the explanatory variables associated with the vitamin D response variables or endothelial function, the logistic regression model was used, according to the definition of the response variable as qualitative. The level of significance used was 5%. The computer program used was R CORE-TEAM, 2020.
Results
Vitamin D Categories
In the sample of this study (n=509), 124 (24.4%) had values below 30 ng/mL and 385 (75.6%) of the participants, above 30 ng/mL.
Endothelial Function Measurements
Descriptive statistics with BPA and PATratio values (Table 1).
Variable
Median
(Q1-Q3)
BPA
6.106
(5.527-6.652)
PATratio
0.464
(0.201-0.769)
BPA Basal Pulse Amplitude and PATratio Peripheral Arterial Tonometry ratio.
Data are presented as median an Q1 and Q2 (interquartile range).
Table 1: BPA and PATratio values of 489 study participants.
In the qualitative measure of endothelial function, the combined values of the BPA and PATratio quartiles were used to classify the endothelial function in the categories worse, moderate and better function. Figure 1 illustrates this classification: quadrant 1 contains the 306 (62.6%) individuals with better endothelial function (BPA<Q3 and PATratio>Q1); quadrant 4, 61 (12.5%) individuals with worse endothelial function (BPA>Q3 and PATratio<Q1); and in quadrants 2 and 3 are the 122 (24.9%) individuals with moderate endothelial function.
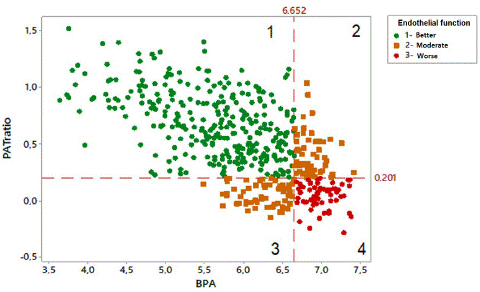
Figure 1: Scatter diagram of BPA Basal Pulse Amplitude and PATratio Peripheral Arterial Tonometry ratio parameters for classification of endothelial function in better (quadrant 1), moderate (2 and 3) or worse (4).
The categorized vitamin D levels were compared to the endothelial function measures given by BPA and PATratio, and with the endothelial function categories in Figure 1. Participants with PATratio<0.2010 had significantly lower vitamin D levels (p=0.031). No difference was observed in biomarker levels between groups with BPA measurements above or below 6.6519. Lower vitamin D levels were observed in the group with worse endothelial function when compared to individuals with moderate or better endothelial function (p=0.040).
Regression Model for Endothelial Function
The ordinal logistic regression model was adjusted for ordered categories (worse, moderate and better) to investigate the association between vitamin D and endothelial function.
The vitamin D variable was introduced as a fixed explanatory variable. The other explanatory variables were chosen among the participants' characteristics and laboratory parameters using the stepwise method of variable selection in regression models.
For each 1 ng/mL increase in serum vitamin D levels, the chance of having better endothelial function increased by 1%. On the other hand, for each additional unit in age, Body Mass Index (BMI) and triglycerides reduces the chance of having better endothelial function increased by 2%, 8% and 1%, respectively. Being male or white or high urine calcium (> 9,5 mg/dL) decrease the chance of having better endothelial function by 72%, 35% and 37% respectively (Table 2).
Characteristics
Odds ratio*
CI 95%
p-value
Vitamin D (ng/mL)
1.01
(1.00;1.01)
0.052
Age (years)
0.98
(0.95;1.00)
0.040
Gender: male
0.28
(0.18;0.40)
0.000
Color/race: white
0.65
(0.45;0.96)
0.031
BMI (Kg/m2)
0.92
(0.90;0.98)
0.004
Triglycerides (mg/dL)
0.99
(0.99;1.00)
0.009
Urine calcium >9,5 mg/dL
0.63
(0.43;0.93)
0.020
*Better to worse endothelial function. BMI: Body Mass Index
Table 2: Logistic regression model for endothelial function according to vitamin D and characteristics of study participants.
Discussion
Vitamin D and Endothelial Function Measures
Participants with worse endothelial function had lower blood vitamin D when compared to those with better or moderate endothelial function. Accordingly, this finding was also reported in other studies that used different techniques to assess endothelial function [13-15]. Jablonski, 2011 [14], demonstrated that individuals with vitamin D deficiency have lower expression of the Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) and 1-a-hydroxylase in endothelial cells when compared to healthy individuals [14]. Therefore, decreased levels of vitamin D may be associated with less vascular protection, being a possible indicator of poorer vascular health or microvascular damage.
Logistic Regression: Endothelial Function and Characteristics of Study Participants
Through logistic regression analysis, the variables that affect both endothelial function and vitamin D blood levels of the study participants were evaluated. According to the model used, being male, increasing in age, BMI, triglycerides, and urinary calcium reduces the chance of the individual having better endothelial function, which can be considered as factors with a negative impact on the endothelium health. On the other hand, being of black, brown, yellow or indigenous color/race, as well as the increase in the serum concentration of vitamin D indicated an increase in the chance of better endothelial function; supporting the hypothesis once again that vitamin D exerts a protective action to vascular health.
Conclusion
Although there is biological plausibility in the association between vitamin D deficiency and endothelial dysfunction, the cross-sectional study (study design) is fragile in establishing a cause-effect relationship, as there is no clear temporal sequence between vitamin D blood concentration and endothelial function. This may be an interesting point to be highlighted as a limitation of the study. On the other hand, as a positive factor, the sample size is highlighted.
Author Statements
Conflict of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical Statement
The ELSA-Brasil study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at each participating institution and at the Brazilian National Research Ethics Committee. The Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais approval is under the number 186/06. We certify that the study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments, and the Resolution 466/12, from the Brazilian National Health Council.Informed consent All participants agreed and signed the informed consent before any study procedures.
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful to Caixa de Assistência Universitária (CASU) and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerias (FAPEMIG) for support and funding. The authors would like to thank the patients who participated in this study.
Author Contributions
Authorship contribution statement. Sousa MCR: Writing - Review & Editing. Silva IFO: Writing - Review & Editing. Reis EA: Formal analysis. Ribeiro ALP: Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. Brant LCC: Selection randomly participants for reassessment and Digital vascular measures. Gonçalves LG: Supervision, Project administration. Barreto S: Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Funding
The ELSA-Brasil baseline study was supported by the Brazilian Ministry of Health (Science and Technology Department) and the Brazilian Ministry of Science and Technology (Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos) and CNPq National Research Council; grants of baseline 01 06 0010.00 RS, 01 06 0212.00 BA, 01 06 0300.00 ES, 01 06 0278.00 MG, 01 06 0115.00 SP, 01 06 0071.00 RJ. Dr Brant is supported in part by CNPq 307329/2022-4.
References
- Apostolakis M, Armeni E, Bakas P, Lambrinoudaki I. Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease. Maturitas. 2018; 115: 1-22.
- Grübler MR, März W, Pilz S, Grammer TB, Trummer C, Müllner C, et al. Vitamin-D concentrations cardiovascular risk and events – a review of epidemiological evidence. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2017; 18: 259-72.
- Jamali N, Sorenson CM, Sheibani N. Vitamin D and regulation of vascular cell function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018; 314: H753-65.
- Kim DH, Meza CA, Clarke H, Kim JS, Hickner RC. Vitamin D and endothelial function. Nutrients. 2020; 12: 1-17.
- Alyami AM, Lam V, Soares MJ, Zhao Y, Sherriff JL, Mamo JC, et al. The association of vitamin D status with dyslipidaemia and biomarkers of endothelial cell activation in older Australians. Nutrients. 2016; 8: 1-8.
- Hussin AM, Mathers JC, Hill T, Siervo M. Cross-sectional study to evaluate the association between vitamin D status and endothelial function in overweight and obese, post-menopausal women. Proc Nutr Soc. 2016; 75: OCE3.
- Hussin AM, Ashor AW, Schoenmakers I, Hill T, Mathers JC, Siervo M. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on endothelial function: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Eur J Nutr. 2017; 56: 1095-104.
- Nemerovski CW, Dorsch MP, Simpson RU, Bone HG, Aaronson KD, Bleske BE. Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease. Pharmacotherapy. 2009; 29: 691-708.
- Bouillon R. Comparative analysis of nutritional guidelines for vitamin D. Rev Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017; 8: 466-79.
- Hymøller L, Jensen SK. Vitamin D analysis in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with C30 reversed phase column and UV detection-Easy and acetonitrile-free. J Chromatogr A. 2011; 1218: 1835-41.
- Brant LCC, Barreto SM, Passos VMA, Ribeiro ALP. Reproducibility of peripheral arterial tonometry for the assessment of endothelial function in adults. J Hypertens. 2013; 31: 1984-90.
- Brant LCC, Hamburg NM, Barreto SM, Benjamin EJ, Ribeiro ALP. Relations of digital vascular function, cardiovascular risk factors, and arterial stiffness: the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil) cohort study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014; 3: e001279.
- Ertek S, Akgül E, Cicero AF, Kütük UT, Demirtas S, Cehreli S, et al. 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels and endothelial vasodilator function in normotensive women. Arch Med Sci. 2012; 8: 47-52.
- Jablonski KL, Chonchol M, Pierce GL, Walker AE, Seals DR. 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency is associated with inflammation-linked vascular endothelial dysfunction in middle-aged and older adults. Hypertension. 2011; 57: 63-9.
- Tanaka K, Okada Y, Hajime M, Tanaka Y. Low vitamin D levels are associated with vascular endothelial dysfunction in patients with poorly controlled Type 2 diabetes: A retrospective study. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2022; 29: 242-51.