
Research Article
Austin J Nutr Metab. 2025; 12(1): 1137.
Perspective on the Potential Efficacy of ONWAY® as a Therapeutic Agent for COVID-19: Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analyses
Yang F, Dong J* and Wei J*
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Medicine, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093, China
*Corresponding author: Jiwu Wei, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Medicine, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093, China Email: wjw@nju.edu.cn
Jie Dong, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Medicine, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093, China Email: dongjie@nju.edu.cn
Received: January 08, 2025; Accepted: January 28, 2025; Published: February 03, 2025
Abstract
Background: COVID-19 is rapidly spreading worldwide. Targeting Akt has emerged as a hopeful approach for treating COVID-19, providing possible therapeutic benefits when focused on specifically. Prior research has confirmed that the active constituents of ONWAY® exhibit a robust attraction to the active region of Akt, consequently impeding the regular operation of its subsequent pathway. Hence, the objective of this ongoing investigation was to assess the feasibility of utilizing ONWAY® as a potential remedy for COVID-19.
Subjects and Methods: The ONWAY® target and the gene set associated with the novel coronavirus were generated by utilizing the pharmacology database of the Chinese Traditional Medicine system and seven disease gene databases. To elucidate the underlying mechanisms, we conducted gene ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis, and protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis. Additionally, molecular docking was employed to observe the interaction patterns between active compounds and specific proteins.
Results: A total of 124 genes were generated, surpassing the established efficacy of Lianhua Qingwen capsule in fighting against COVID-19. Subsequently, a network was established by linking 197 active substances with 468 pairs of compound-target connections. Through the examination of GO and KEGG pathways, it was discovered that ONWAY® exerts regulatory influences on immune response, apoptosis, and viral infection. Four central genes were identified by utilizing the PPI network and subnetworks. Molecular docking was performed on four genes, namely ALB, Akt1, IL-6, and TNF. The presence of these genes is linked to lung damage, the development of lung fibrosis, and viral infection. Importantly, ONWAY® includes two active substances, specifically quercetin and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, that have the ability to penetrate the active cavity of these four proteins. As a result, they show encouraging therapeutic characteristics in regards to COVID-19.
Conclusions: From a bioinformatics standpoint, the study findings elucidate the potential medicinal applications of ONWAY® in managing COVID-19. Furthermore, the research provides insights into the mode of operation of ONWAY®, thereby supporting the advancement of specific drug development and promoting fundamental studies on SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: Chinese traditional medicine; COVI-19, ONWAY®, Molecular docking; Network pharmacology
Highlights
ONWAY® has a total of 124 (872) focal points dedicated to COVID-19 disease targets.
ONWAY® was considered to have Quercetin and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate as its potential bioactive components in the fight against COVID-19.
ONWAY® combats COVID-19 by controlling the immune response, promoting apoptosis, and inhibiting virus infection.
The ability of ONWAY® to inhibit COVID-19 may be due to its small molecule's selective binding to ALB, Akt1, IL-6, and TNF, which contributes to its mechanism of action.
Introduction
COVID-19, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, is a highly contagious respiratory illness characterized by symptoms such as fever, fatigue, dry throat, organ dysfunction, and in severe cases, death. Between July 31 and August 27, 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported a 38% increase in cases, with over 1.4 million new infections and more than 1,800 deaths. By August 27, 2023, over 770 million confirmed cases and over 6.9 million deaths had been recorded globally [1].
Amidst the ongoing global pandemic, the National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China reported that more than 90% of COVID-19 patients exhibited positive responses to combined treatment with Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and Western Medicine, leading to recovery or significant improvement [2]. Early use of TCM has been shown to be effective in preventing the progression of mild and moderate cases to severe or critical stages, and in severe cases, TCM has been demonstrated to stabilize the patient, extending the time for treatment [3]. Increasing evidence supports the role of early TCM intervention in improving recovery rates, shortening illness duration, slowing disease progression, and reducing mortality in COVID-19 patients [4-6]. A comprehensive analysis conducted by the State Council Information Office in China identified three TCM decoctions and three Chinese patent medicines, collectively referred to as the "six most effective recipes," as the most efficacious treatments for COVID-19 patients in China [7]. These formulas include Jinhua Qinggan granules (JHQG), Lianhua Qingwen capsules (LHQW), Lung Cleansing and Detoxifying Decoction (LCDD) (also known as Qingfei Paidu, QFPD), Xuanfeibaidu granules (XFB), Huashibaidu granules (HSBD), and Xuebijing (XBJ) [7]. Through network pharmacology analysis, it was found that LHQW targets 65 proteins associated with COVID-19, with a strong affinity for Akt1, a key protein involved in the disease process [8]. Research has shown that Akt activation during SARS-CoV-2 infection is dose-dependent [9]. Additionally, the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway plays a significant role in lung damage, pulmonary fibrosis, and immune cell maturation [10].
ONWAY®, a Traditional Chinese Medicine solid beverage, is made from water extracts of eight "medicinal and edible" herbs: Ginkgo nut, Dahurian angelica, Olive, Lobed kudzu root, Honeysuckle, Fig, Setose thistle, and Mongolian dandelion. Previous studies have shown that the active components of ONWAY® exhibit a strong binding affinity for Akt1. To evaluate the potential efficacy of ONWAY® in treating COVID-19, we conducted an analysis of drug-target interactions, disease-target interactions, and key target proteins in both the ONWAY® and COVID-19 contexts. The study employed Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway and Gene Ontology (GO) analyses, along with protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks and molecular docking methods. Our findings suggest that, in addition to Akt1, ONWAY® exhibits significant binding affinity to the active sites of IL-6, TNF, and ALB, which are recognized targets in the pathogenesis of COVID-19. These results provide evidence for ONWAY®'s potential as an effective therapeutic option for COVID-19.
Materials and Methods
Acquiring Data for ONWAY® and COVID-19 Genes
We gathered information on ONWAY®’s active compounds and target genes from the TCMSP database, applying criteria of oral bioavailability (OB) > 30% and drug-likeness (DL) > 0.18. The target genes for each compound were retrieved using Uniprot. For COVID- 19-related genes, we searched six databases: GeneCards, OMIM, TTD, DrugBank, DisGeNet, and PubChem, and combined the findings to create a gene set specific to COVID-19.
Network Construction
We used Cytoscape to build a network linking ONWAY®’s target genes to COVID-19-related genes, based on the overlap of the two gene sets.
Gene Ontology (GO) and KEGG Pathway Analysis
GO and KEGG pathway analyses were conducted to identify the biological processes and signaling pathways associated with ONWAY®'s effects on COVID-19, using R and Metascape.
Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
A PPI network was constructed using Cytoscape, focusing on key therapeutic targets based on interaction degree values. CytoHubba and CytoNCA plugins were used to identify the top 10 essential proteins.
Molecular Docking
For molecular docking, we selected the most important gene from the PPI network. The 3D structure of the receptor protein was obtained from the RCSB PDB database, and the corresponding ligand structures were sourced from PubChem. Energy minimization and docking were performed using ChemBio 3D, PyMOL 2.4.0, and Autodock Vina to analyze the binding affinity between ONWAY®'s active compounds and the receptor proteins. These methods allowed us to explore the therapeutic potential of ONWAY® for COVID-19 through its interaction with key molecular targets.
Results
Evaluation of Active Substances and Possible Objectives
In total, 57 bioactive candidates of ONWAY® were selected for further analysis. Additionally, Ginkgo nut had 14 active compounds, Dahurian angelica had 21 active compounds, Olive had 2 active compounds, Lobed kudzuvine root had 4 active compounds, Honeysuckle had 22 active compounds, Fig had 5 active compounds, Setose thistle had 5 active compounds, and Mongolian dandelion had 6 active compounds (Table 1). Furthermore, 494 targets were obtained of these 57 active compounds in ONWAY® (Extended data 1). In addition, we acquired 288, 1, 44, 31, 542, and 179 genes associated with COVID-19 from the databases Genecards, OMIM, TTD, DrugBank, DisGeNet, and PubChem, respectively. A combined total of 872 gene sets linked to COVID-19 were acquired by consolidating the search results and removing duplicates (as depicted in Figure 1A and Extended data 2). Through the identification of genes that coincide between compound-target genes and genes associated with diseases, we successfully acquired a collection of 124 genes encompassing the ONWAY® target and genes linked to COVID-19. The gene count in this surpasses the previously established Lianhua Qingwen capsule by an additional 56 genes (Figure 1B and Extended data 3).
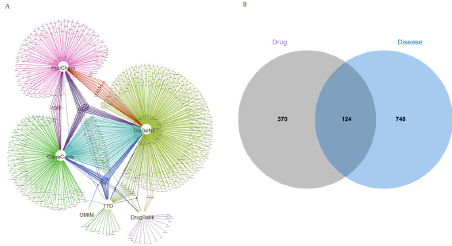
Figure 1: Identifying the interaction between drugs and their targets.
A. The COVID-19 genes are identified by combining the findings from six
databases. B. The disease-associated genes linked to the drug target are
identified by finding the common genes between the ONWAY® target genes
and the genes related to COVID-19.
Compound-Target Network
In order to elucidate the primary components that ONWAY® focuses on in relation to COVID-19, a visual representation of a network linking active substances, illnesses, and objectives was generated, as depicted in Figure 2A. The network, which represents the interaction between compounds and target diseases by identifying associated genes, was visualized using Cytoscape 3.9.1. It consisted of 197 nodes and 468 edges. Based on network analysis, the average degree of all candidate compounds was 4.751, as depicted in Figure 2A. Generally, it is widely noted that a solitary gene can be focused on by numerous effective substances, while a solitary substance can target multiple genes. Among the 124 genes analyzed, PTGS 2 emerged as the gene most frequently targeted by the ingredients of ONWAY®.
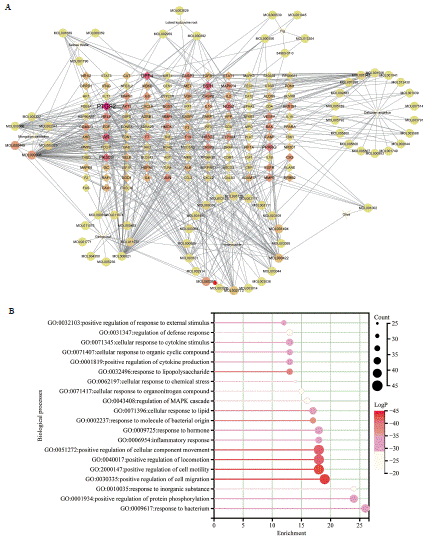
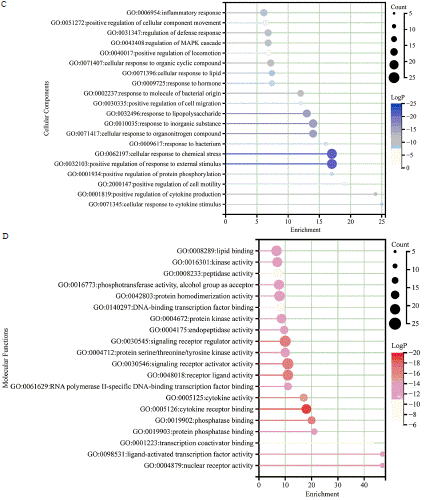
Figure 2: The drug-target pharmacology network construction and the subsequent analysis of GO enrichment. A. The drug-target pharmacology network
construction and the subsequent analysis of GO enrichment. The network illustrates the correlation between active compounds of Traditional Chinese Medicine
(TCM) components in ONWAY® and the target genes associated with COVID-19. The small molecule compounds are represented by circles, the target genes
are represented by quadrangles, and the interactions between them are represented by edges. The intensity of the color in the network increases with the degree
of connectivity. B-D. The sentence could be revised as follows: The present study conducted a GO enrichment analysis on the target genes. Enrichment in this
context denotes the relative probability of actual enrichment compared to random enrichment, while counts represent the quantity of enriched genes.
In Table 2, the degree values of the top 6 active components are shown, with 2 compounds having degree values higher than 50: quercetin (degree=65) and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (degree=52). As a result, these substances were considered as possible active substances of ONWAY® in the fight against COVID-19.
GO Enrichment Analysis
To perform a more thorough investigation into the possible impact of ONWAY® on COVID-19, we analyzed the biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF) terms linked to the common targets. Extended data 4 reported a significant enrichment of 1890 GO terms (P<0.01), including 1694 BP terms, 69 CC terms, and 127 MF terms. Additionally, we provide a table (Table 3) displaying 5 GO BP terms that are relevant to viral invasion, as suggested by the findings of the enrichment analysis. This indicates that these specific genes have a vital function in the infection induced by the virus. Figure 2B displays the top 20 terms that are significantly enriched in the BP, CC, and MF categories. The results suggest that the main BP terms consist of promoting cell migration, promoting cell motility, promoting movement of cellular components, promoting locomotion, reacting to lipopolysaccharide, reacting to molecules of bacterial origin, and responding to lipids. The primary CC terms include lipid raft, membrane microdomain, vesicle interior, secretory granule interior, cytoplasmic vesicle interior, and endoplasmic reticulum interior. In conclusion, the primary MF concepts include binding to cytokine receptors, activating signaling receptors, regulating signaling receptors, ligand activity of receptors, binding to phosphatases, and cytokine activity.
KEGG Enrichment Analysis
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis was conducted on 124 commonly targeted genes, revealing the identification of 143 pathways (P<0.01). This indicates the influence of these target genes on various pathways related to bacterial and viral infection, immune cell differentiation, signal transmission, and significant pathological processes including apoptosis (Figure 3A and Extended data 5). The pathway map of the MAPK was visually depicted in Figure 3B. Additionally, Table 4 showcased the extracted pathways associated with viruses
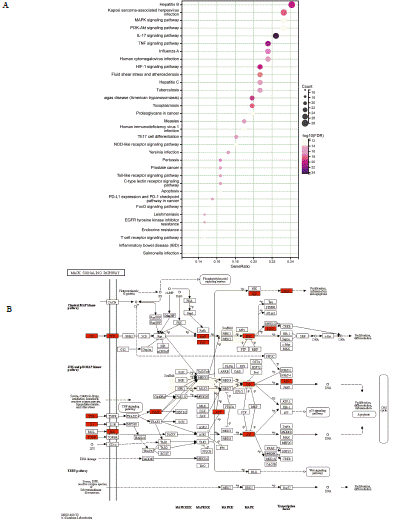
Figure 3: KEGG enrichment analysis and pathway map. A. KEGG enrichment analysis was conducted on the target genes, assessing the comparative
likelihood of actual enrichment in comparison to random enrichment. The counts of enriched genes were also determined. B. The pathway map of MAPK was
identified as one of the most significant enriched pathways.
PPI Network and Core Subnetwork
To offer a thorough comprehension of how ONWAY® impacts COVID-19, we employed a protein-protein interaction network obtained from the STRING database. The network displayed complex connections among the proteins produced by the specified genes (Figure 4A, B). Afterwards, we brought the PPI network into Cytoscape for further examination. In the end, CytoNca and CytoHubba identified two important subnetworks comprising of 10 target genes each (Figure 5A-B).
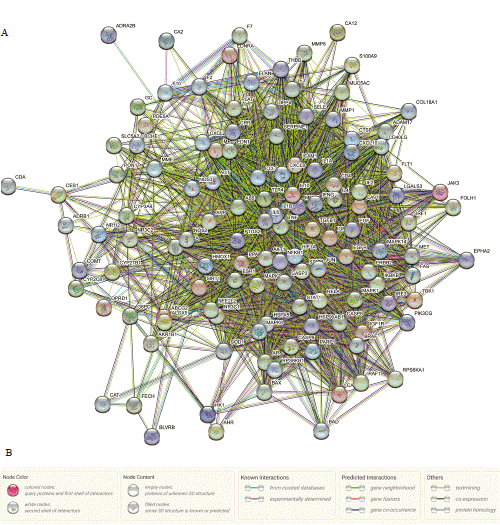
Figure 4: Protein-Protein interaction (PPI) network. A. The PPI network was acquired from the STRING database. B. Annotations are given for both the
nodes and edges in the PPI network.
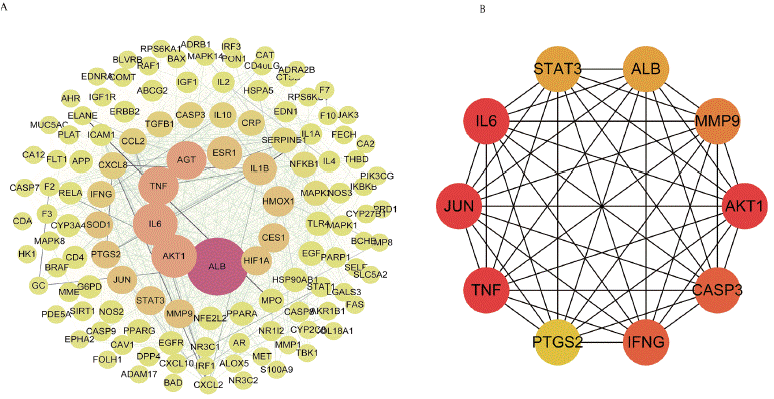
Figure 5: Using Cytoscape, the key subnetwork was identified. A. The PPI network was filtered using CytoNca. The dots’ dimensions and luminosity augment
in accordance with the network’s betweenness. The ten most central points are responsible for the network’s highest betweenness values. As the network coexpression
value increases, the line’s width and depth are seen to enhance. B. Key subnetwork analyzed by CytoHubba, focusing on the top 10 nodes.
Molecular Docking of Active Compounds and Selected Proteins
To conduct molecular docking analysis, four genes, namely ALB (albumin), AKT1 (AKT serine/threonine kinase 1), IL-6, and TNF, were chosen by evaluating the overlap between the two primary subnetworks (Figure 6A). Two bioactive compounds, specifically quercetin and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, were identified from the network of compound-target interaction. These compounds exhibited promising affinity towards the mentioned proteins. Figure 6B-I illustrates that the active compounds effectively entered and bound to the active cavity of all four proteins, as indicated by the results obtained from molecular docking simulations. Figure 7 displays the docking scores using a heat map visualization.
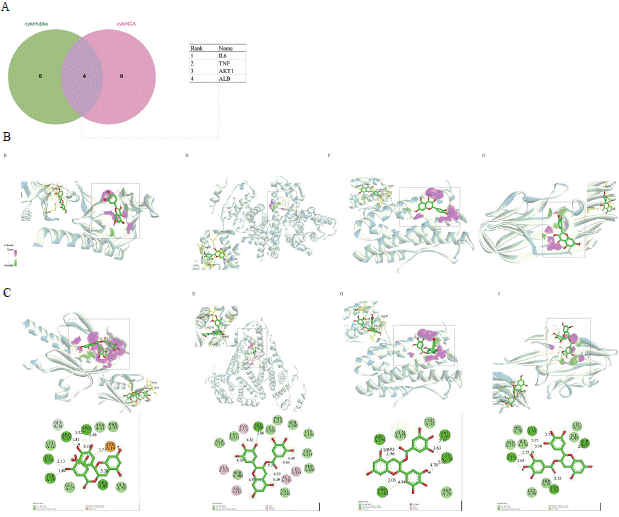
Figure 6: Screening and molecular docking of the essential genes within the subnetwork. A. The key genes were screened by intersecting the two key
subnetworks. The process of molecular docking includes the interaction between proteins and small molecule ligands. The top part of the diagram illustrates
the three-dimensional arrangement of the ligands and receptors, along with the surface of the receptor. Conversely, the lower portion illustrates a 2D schematic
diagram representing the docking model of ligands with proteins. The molecular docking outcomes involving quercetin and AKT1. (B). (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate
and AKT1 (C), quercetin and ALB (D), (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and ALB (E), quercetin and IL-6 (F), (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and IL-6 (G), quercetin and
TNF (H), and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and TNF (I) were visualized.

Figure 7: Molecular docking score heat-map.
Discussion
The ongoing global spread of SARS-CoV-2 continues to challenge healthcare systems worldwide, particularly due to the lack of fully effective treatments. Notably, China, with a population of over 1.3 billion, has successfully managed transmission, in part due to the use of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), which has shown significant efficacy in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 [6,11-12]. This study evaluates the potential of ONWAY®, a self-formulated solid beverage made from the aqueous extract of eight medicinal and edible herbs, in managing COVID-19. By analyzing the active components of these herbs, we identified a target gene set of 124 genes associated with COVID-19, which is notably larger than the 10 genes targeted by LHQW. Our network analysis confirmed key compound-target pairs, and Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses revealed that ONWAY® influences immune pathways critical to viral defense.
Further protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis identified four hub targets among the 124 genes. Molecular docking studies confirmed interactions between ONWAY® components and targets such as ALB, Akt1, IL-6, and TNF, supporting ONWAY®'s potential therapeutic effects against COVID-19. These findings suggest that ONWAY® may enhance immune responses and potentially mitigate viral replication.
The significance of these results is underscored by the role of key components like honeysuckle, angelica, and dandelion, which have demonstrated antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects in prior studies. Their synergy with oseltamivir in treating influenza A also supports their potential in managing COVID-19. Our analysis of the 20 leading GO terms indicates that ONWAY® may modulate the oxidative stress pathway, which plays a significant role in the pathophysiology of severe COVID-19. Overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is known to contribute to tissue damage in COVID-19 patients [13], and ONWAY®'s potential to reduce oxidative stress could provide a therapeutic advantage. Additionally, the enrichment of target genes in MAPK pathways aligns with research indicating the role of p38 MAPK in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Elevated p38 MAPK activity has been linked to higher levels of IL-8 and may contribute to inflammatory responses and cell death during infection [15-16]. Moreover, ONWAY®'s impact on the MAPK pathway suggests its potential to modulate platelet activation, which is associated with thrombosis and inflammation in COVID-19 [17].
Akt1, a key protein in the PI3K/Akt pathway, has been shown to play a crucial role in viral protein synthesis and immune cell function. Its activation promotes immune responses but excessive Akt1 activity may lead to T-cell exhaustion and poor outcomes in viral infections, including COVID-19 [18-26]. Our findings suggest that ONWAY® could help regulate Akt1 activation, thereby modulating immune responses and improving prognosis in COVID-19 patients.
Furthermore, ALB, which is vital for immune function and nutritional balance, is negatively correlated with poor outcomes in COVID-19 [27]. The interaction between ONWAY® components and ALB highlights its potential to support immune function in COVID-19 patients, particularly by reducing inflammatory cytokines like TNF and IL-6, which are central to the cytokine storm observed in severe COVID-19 cases [29-31].
Our molecular docking analysis further confirmed interactions between Akt1, TNF, IL-6, and the active compounds in ONWAY®. These findings underline the potential of ONWAY® in modulating inflammation and immune responses. The results provide a pharmacological basis for ONWAY®'s therapeutic potential in treating COVID-19 and offer insights for the development of new antiviral agents.
In conclusion, this study suggests that ONWAY® could play a significant role in managing COVID-19 by modulating immune responses, reducing inflammation, and targeting key viral pathways. However, further investigation into the mechanisms of its active compounds is essential to fully understand its potential and develop more effective antiviral treatments.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation No. 2020M671444 and National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) No. 81330088.
Author Contributions
FM. Yang contributed to the development and planning of the research. FM. Yang, JW. Wei, and J. Dong conducted the network pharmacology and bioinformatic analyses and authored the article. The manuscript was reviewed by FM. Yang and J. Dong, and subsequently approved as the final version.
References
- WHO. Global research on coronavirus disease (COVID-19). 2023.
- Daily C. 6 effective TCM recipes for COVID-19. 2020.
- Ren JL, Zhang AH, Wang XJ. Traditional Chinese medicine for COVID-19 treatment[J]. Pharmacol Res. 2020; 155: 104743.
- Chen G, Su W, Yang J, et al. Chinese herbal medicine reduces mortality in patients with severe and critical Coronavirus disease 2019: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Front Med. 2020;14: 752-759.
- Li ZY, Xie ZJ, Li HC, et al. Guidelines on the treatment with integrated traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine for severe coronavirus disease 2019[J]. Pharmacol Res. 2021; 174: 105955.
- Liu M, Gao Y, Yuan Y, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine for Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Pharmacol Res. 2020; 158: 104896.
- Luo H, Gao Y, Zou J, et al. Reflections on treatment of COVID-19 with traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chin Med. 2020; 15: 94.
- Xia QD, Xun Y, Lu JL, et al. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analyses on Lianhua Qingwen capsule indicate Akt1 is a potential target to treat and prevent COVID-19[J]. Cell Prolif. 2020; 53: e12949.
- Appelberg S, Gupta S, Svensson Akusjärvi S, et al. Dysregulation in Akt/ mTOR/HIF-1 signaling identified by proteo-transcriptomics of SARS-CoV-2 infected cells[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020; 9: 1748-1760.
- Chen H, Chen N, Li F, et al. Repeated radon exposure induced lung injury and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in human bronchial epithelial cells and mice[J]. Toxicol Lett. 2020; 334: 4-13.
- Li X, Yang Y, Liu L, et al. Effect of combination antiviral therapy on hematological profiles in 151 adults hospitalized with severe coronavirus disease 2019[J]. Pharmacol Res. 2020; 160: 105036.
- Xiao M, Tian J, Zhou Y, et al. Efficacy of Huoxiang Zhengqi dropping pills and Lianhua Qingwen granules in treatment of COVID-19: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Pharmacol Res. 2020; 161: 105126.
- Schönrich G, Raftery MJ, Samstag Y. Devilishly radical NETwork in COVID-19: Oxidative stress, neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), and T cell suppression[J]. Adv Biol Regul. 2020; 77: 100741.
- Dyankov G, Genova-Kalou P, Eftimov T, et al. Binding of SARS-CoV-2 Structural Proteins to Hemoglobin and Myoglobin Studied by SPR and DR LPG[J]. Sensors (Basel). 2023; 23: 3346.
- Lee CH, Chen RF, Liu JW, et al. Altered p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase expression in different leukocytes with increment of immunosuppressive mediators in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome[J]. J Immunol. 2004; 172: 7841-7847.
- Mizutani T. Signal transduction in SARS-CoV-infected cells[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007; 1102: 86-95.
- Zhang S, Liu Y, Wang X, et al. SARS-CoV-2 binds platelet ACE2 to enhance thrombosis in COVID-19[J]. J Hematol Oncol. 2020; 13: 120.
- Wang X, Zhang H, Abel AM, et al. Role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and Akt1 kinase in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) replication[J]. Arch Virol. 2014; 159: 2091-2096.
- Kindrachuk J, Ork B, Hart BJ, et al. Antiviral potential of ERK/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling modulation for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection as identified by temporal kinome analysis[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015; 59: 1088-1099.
- Zhang Y, Wang X, Yang H, et al. Kinase AKT controls innate immune cell development and function[J]. Immunology. 2013; 140: 143-152.
- Rogel A, Willoughby JE, Buchan SL, et al. Akt signaling is critical for memory CD8(+) T-cell development and tumor immune surveillance[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017; 114: E1178-E1187.
- Jones N, Vincent EE, Cronin JG, et al. Akt and STAT5 mediate naïve human CD4+ T-cell early metabolic response to TCR stimulation[J]. Nat Commun. 2019; 10: 2042.
- Zhu Z, Shukla A, Ramezani-Rad P, et al. The AKT isoforms 1 and 2 drive B cell fate decisions during the germinal center response[J]. Life Sci Alliance. 2019; 2: e201900506.
- Li M, Lazorchak AS, Ouyang X, et al. Sin1/mTORC2 regulate B cell growth and metabolism by activating mTORC1 and Myc[J]. Cell Mol Immunol. 2019; 16: 757-769.
- Lucas CL, Kuehn HS, Zhao F, et al. Dominant-activating germline mutations in the gene encoding the PI(3)K catalytic subunit p110d result in T cell senescence and human immunodeficiency[J]. Nat Immunol. 2014; 15: 88-97.
- Diao B, Wang C, Tan Y, et al. Reduction and Functional Exhaustion of T Cells in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)[J]. Front Immunol. 2020; 11: 827.
- Richardson DP, Lovegrove JA. Nutritional status of micronutrients as a possible and modifiable risk factor for COVID-19: a UK perspective[J]. Br J Nutr. 2021; 125: 678-684.
- Damayanthi H, Prabani K. Nutritional determinants and COVID-19 outcomes of older patients with COVID-19: A systematic review[J]. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2021; 95: 104411.
- Bode JG, Ehlting C, Häussinger D. The macrophage response towards LPS and its control through the p38(MAPK)-STAT3 axis[J]. Cell Signal. 2012; 24: 1185-1194.
- Ouyang Y, Yin J, Wang W, et al. Downregulated Gene Expression Spectrum and Immune Responses Changed During the Disease Progression in Patients With COVID-19[J]. Clin Infect Dis. 2020; 71: 2052-2060.
- Wen W, Su W, Tang H, et al. Immune cell profiling of COVID-19 patients in the recovery stage by single-cell sequencing[J]. Cell Discov. 2020; 6: 31.
- Xiong Y, Liu Y, Cao L, et al. Transcriptomic characteristics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in COVID-19 patients[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020; 9: 761-770.
- Jo S, Kim S, Shin DH, et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV 3CL protease by flavonoids[J]. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020; 35: 145-151.
- Gandhi GR, Vasconcelos A, Haran GH, et al. Essential oils and its bioactive compounds modulating cytokines: A systematic review on anti-asthmatic and immunomodulatory properties[J]. Phytomedicine. 2020; 73: 152854.
- Southworth T, Mason S, Bell A, et al. PI3K, p38 and JAK/STAT signalling in bronchial tissue from patients with asthma following allergen challenge[J]. Biomark Res. 2018; 6: 14.