
Case Report
Austin Gynecol Case Rep. 2023; 8(2): 1042.
Concurrent Cerebral Thrombophlebitis and Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenoma in a Postpartum Woman: A Rare Coexistence and Diagnostic Challenges
Boubekri A¹*; Bellamlih H²; Ababou M¹; Atmani W¹; Meziane M¹; Jaafari A¹; Baite A¹; Bensghir M¹
¹Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care, Mohammed V University, Morocco
²Radiology Department, Moulay-Ismail Military Hospital, Meknes, Sidi Mohamed Ben Abdellah University, Fez, Morocco
*Corresponding author: Boubekri Ayoub Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care, Mohammed V University, Morocco. Email: dr.boubkri@gmail.com
Received: July 03, 2023Accepted: August 05, 2023 Published: August 13, 2023
Abstract
This case report presents a rare occurrence of concurrent cerebral thrombophlebitis and nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma in a postpartum woman. Cerebral thrombophlebitis is a rare condition that can manifest with diverse clinical presentations, posing diagnostic challenges. The patient, a 30-year-old primipara, presented with progressive vision loss, diplopia, and intense frontal headaches shortly after childbirth. Magnetic resonance angiography revealed thrombophlebitis in the right lateral sinus extending into the ipsilateral internal jugular vein, along with a large suprasellar lesion suggestive of a pituitary macroadenoma. Ophthalmological examination revealed papilledema and ptosis. Laboratory analyses ruled out hormonal abnormalities associated with pituitary adenomas. The patient received intravenous methylprednisolone and therapeutic anticoagulation, resulting in neurological and ophthalmological improvements. Subsequently, the patient underwent transsphenoidal resection. This case highlights the diagnostic and management challenges associated with rare postpartum conditions and emphasizes the importance of comprehensive evaluation and multidisciplinary care in such cases.
Keywords: Cerebral thrombophlebitis; Postpartum; Nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma
Introduction
Cerebral thrombophlebitis is a rare but severe condition that can occur during pregnancy and the postpartum period. It is characterized by a diverse range of clinical presentations, including headaches, seizures, and neurological deficits. The diagnosis of cerebral thrombophlebitis relies heavily on neuroradiological imaging, particularly cerebral Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Treatment primarily involves the administration of anticoagulant therapy. However, the rarity of postpartum cerebral thrombophlebitis poses significant diagnostic challenges due to its variable symptomatology.
In addition to cerebral thrombophlebitis, other conditions may also manifest during the postpartum period. One such condition is Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenoma (NFPA), which refers to infrequent tumors occurring in women of reproductive age. NFPA cases diagnosed and complicated during pregnancy are extremely rare. During pregnancy, the pituitary gland undergoes anatomical and physiological changes, with a significant increase in size observed. However, symptoms such as blurred vision and headaches resulting from physiological enlargement of the pituitary gland are uncommon.
This article aims to present a rare case of a postpartum woman diagnosed with concurrent cerebral thrombophlebitis and nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma. The coexistence of these two conditions in the same individual is exceedingly rare. By providing a detailed account of this unique case, we aim to contribute to the existing scientific knowledge and raise awareness about the diagnostic and management challenges associated with these conditions in the postpartum period.
Observation
A 30-year-old woman, 55 days postpartum, was admitted to the Neurology Department of the military hospital for the management of intracranial hypertension syndrome. The patient had no significant medical history and was a primipara with regular menstrual cycles before pregnancy, without headaches or visual deficits. Symptoms started immediately in the postpartum period with progressive vision loss, onset of diplopia, and intense frontal headaches refractory to symptomatic treatment. Given the context and timing of symptom onset, cerebral thrombophlebitis was suspected, leading to neuroimaging investigations, including magnetic resonance angiography (Figure 1), which revealed right lateral sinus thrombophlebitis extending into the ipsilateral internal jugular vein and a large suprasellar lesion suggestive of a pituitary macroadenoma. Ophthalmologic examination showed visual acuity of 8/10 in the right eye and the presence of ptosis. Fundoscopy revealed stage 1 papilledema. Laboratory analyses were normal for thyroid axis function, and prolactin levels were within normal range for the postpartum period. There were no symptoms of diabetes insipidus, and there were no signs or symptoms of excess Growth Hormone (GH) or cortisol, indicating a non-functioning pituitary adenoma incidentally discovered during the investigation of cerebral thrombophlebitis.
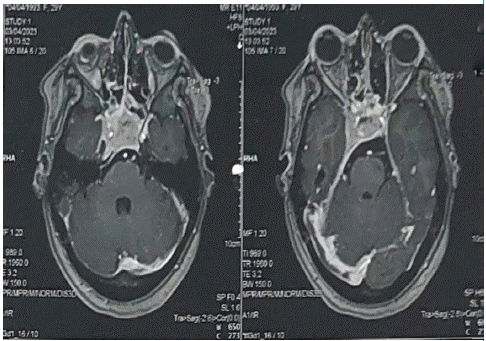
Figure 1: Cerebral MR angiography demonstrates a thrombus in the right lateral sinus with extension into the ipsilateral internal jugular vein, as well as the presence of a macroadenoma of the pituitary gland with extension into the right cavernous sinus.
Intravenous methylprednisolone and therapeutic anticoagulation were administrated, which resulted in neurological and ophthalmological improvements within a few days. The patient was subsequently referred to a neurosurgery department where she underwent transsphenoidal resection.
Discussion
During pregnancy and the postpartum period, the average incidence of Cerebral Thrombophlebitis (CTP) is 10 to 20% of all instances of thrombophlebitis [1]. These episodes are most common within ten weeks following labor, with a peak occurrence between the fourth and twenty-first day, as in the case of our patient, who had symptoms within the first week after delivery. It should be emphasized, however, that earlier or later incidents have also been documented [1]. While cerebral thrombophlebitis can occur at any stage of life, women are particularly vulnerable before and after childbirth due to the physiological changes associated with pregnancy, which contribute to a hypercoagulable state [2].
The signs and symptoms of cerebral thrombophlebitis can differ depending on where the venous thrombosis is located. The clinical appearance of gravidopuerperal cerebral thrombophlebitis, on the other hand, is comparable to the typical picture, with headaches being the most prominent feature. Seizures, localized or bilateral neurological impairments, altered consciousness, and papilledema may also be present [3-5], which can lead to confusion with other neurological or neurosurgical conditions that were not known prior to childbirth [6]. Although Computed Tomography (CT) scanning of the brain is widely utilized as an initial diagnostic tool, when available, cerebral Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) combined with venous Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) is the gold standard for early identification of CTP [7]. In the case of our patient, this diagnostic approach was employed, leading to a definitive diagnosis. With advancements in diagnostic techniques, early initiation of anticoagulant therapy has improved the prognosis of this condition, which was initially associated with poor outcomes, and now patients have a better chance of recovery with near-complete neurological restoration [1].
To the best of our knowledge, there are no reported cases in the literature of the simultaneous occurrence of lateral sinus thrombophlebitis and nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma during the gravidopuerperal period. While prolactinomas are the most prevalent pituitary tumors linked with pregnancy, Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenomas (NFPA) are uncommon in reproductive-age women, with just a few instances detected and complicated during pregnancy [8]. NFPA are frequently difficult to detect clinically until they reach a size large enough to produce symptoms due to mass effect [9,10]. Approximately 50% of NFPA cases are incidentally detected when MRI is performed for other reasons [11], In our situation, an MRI was performed to evaluate probable cerebral thrombophlebitis before the co-occurrence of both illnesses was detected.
50 to 60% of patients with macroadenomas had visual field abnormalities at the time of diagnosis, and 30% to 40% experience headaches [12]. In our case, the patient presented with visual field abnormalities, which could be attributed to both the macroadenoma and the thrombophlebitis, making it challenging to differentiate between the two conditions. When possible, transsphenoidal excision is used as the primary treatment for these malignancies [13,14]. Stereotactic radiation is used to treat and prevent recurrences as well as to shrink post-surgical leftovers [15]. It has not been demonstrated that pharmacological treatment with somatostatin receptor ligands and/or dopamine agonists successfully reduces tumor size [10,15,16].
Conclusion
In conclusion, this rare case of concurrent cerebral thrombophlebitis and nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma in a postpartum woman highlights the diagnostic and therapeutic challenges associated with these rare conditions. Brain imaging, anticoagulant therapy, and multidisciplinary collaboration are crucial for accurate diagnosis and optimal management. This case study contributes to the existing literature and underscores the importance of an integrated approach to improve outcomes in postpartum women with rare neurological manifestations. Further research is needed to deepen our understanding and optimize the management of these conditions.
References
- Kouach J, Mounach J, Moussaoui D, Belyamani L, Dehayni M. Akinetic mutism revealing postpartum cerebral venous thrombosis. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2010; 29: 167-8.
- Cole B, Criddle LM. A case of postpartum cerebral venous thrombosis. J Neurosci Nurs. 2006; 38: 350-3.
- Ferro JM, Canhão P, Stam J, Bousser MG, Barinagarrementeria F, ISCVT Investigators. Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: results of the International Study on cerebral vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis (ISCVT). Stroke. 2004; 35: 664-70.
- Cantú C, Barinagarrementeria F. Cerebral venous thrombosis associated with pregnancy and puerperium. A review of 67 cases. Stroke. 1993; 24: 1880-4.
- Wasay M, Bakshi R, Bobustuc G, Kojan S, Sheikh Z, Dai A et al. Cerebral venous thrombosis: analysis of a multicenter cohort from the United States. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008; 17: 49-54.
- Cordonnier C, Lamy C, Gauvrit JY, Mas L, Leys D. Cerebrovascular pathology of pregnancy and the postpartum period. EMC Neurol, Paris. 2006, Elsevier SAS: 17-046-S10.
- Leach JL, Fortuna RB, Jones BV, Gaskill-Shipley MF. Imaging of cerebral venous thrombosis: current techniques, spectrum of findings, and diagnostic pitfalls. RadioGraphics. 2006; 26: S19-41.
- Caron P, Broussaud S, Bertherat J, Borson-Chazot F, Brue T, Cortet-Rudelli C, et al. Acromegaly and pregnancy: a multicenter retrospective study of 59 pregnancies in 46 women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95: 4680-7.
- Molitch ME. Nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas and pituitary incidentalomas. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2008; 37: 151-71.
- Jaffé CA. Clinically nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma. Pituitary. 2006; 9: 317-21.
- Nielsen EH, Lindholm J, Laurberg P, Bjerre P, Christiansen JS, Hagen C, et al. Nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas: incidence, causes of death, and quality of life in relation to pituitary function. Pituitary. 2007; 10: 67-73.
- Fernandez A, Karavitaki N, Wass JA. Prevalence of pituitary adenomas: a community-based, cross-sectional study in Banbury (Oxfordshire, UK). Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2010; 72: 377-82.
- Laws ER, Thapar K. Pituitary surgery. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1999; 28: 119-31.
- Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, de Divitiis E. Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery. Neurosurgery. 2004; 55: 933-40.
- Losa M, Mortini P, Barzaghi R, Franzin A, Giovanelli M. Inactive and gonadotroph pituitary adenomas: diagnosis and management. J Neurooncol. 2001; 54: 167-77.
- Vieira L Neto, Boguszewski CL, Araújo LA, Bronstein MD, Miranda PA, Musolino NR, et al. A review on the diagnosis and treatment of patients with clinically nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas by the Department of Neuroendocrinology of the Brazilian Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2016; 60: 374-90.