Abstract
A 29-year-old male with pathologically confirmed extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma of the tonsil, nasal type was admitted to Xinhua hospital affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine. The patient was provided with several cycles of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy and obtained a Complete Response (CR) outcome. Despite the response, the patient also suffered from severe adverse effects, including a worsening pulmonary inflammation and severe laryngeal edema. A tracheotomy was performed to remove the white pseudo-membrane of laryngeal. via pathological analysis, necrosis of granuloma lymphoid cells and rhabdomous granuloma was found in this removed section. Meantime, a large amount of Candida nivaria, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and carbapenem-resistant Enterobacter was present in the patient’s sputum culture. The level of inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-a, IL-1, IL-6, IL-17 and IFN-γ,) also increased significantly, indicating immune-related adverse events. Subsequently, the doctors adjusted immunotherapy to single-agent chemotherapy with additional anti-fungal and anti-bacterial infection treatment. The infection was well under control after these adjustments. 18F-FDG PET/ CT recorded the series of changes in the course of the patient from the start of immunotherapy.
Keywords: NK/T cell lymphoma; Immunotherapy; Adverse effects; 18F-FDG PET/CT
Case Report
Treatment with Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICIs), such as anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1, has shown efficacy against diverse types of cancers. In response to the ICI treatments immune-related adverse events, such as infections, can result in severe consequences and often require immediate attention (Figures 1-3) [1-3]. Little is known about how the administration of ICIs affects the onset and progression of infections [1,4]. In our case, the patient had protracted infection including Klebsiella pneumonia, Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacter, Candida nivariensis, all of which may have been associated with the treatment of anti-PD-1 [5-8].
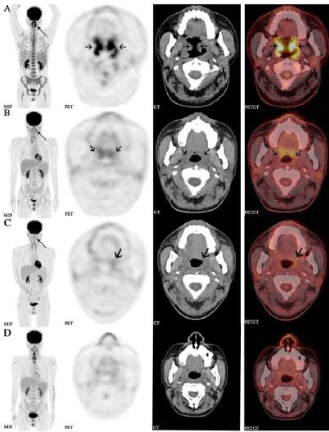
Figure 1: The patient was provided with several cycles of PD1 immunotherapy
followed by staging 18F-FDG PET/CT scans after each treatment. From left
to the right are coronal slices of MIP, PET, CT and fused PET/CT separately,
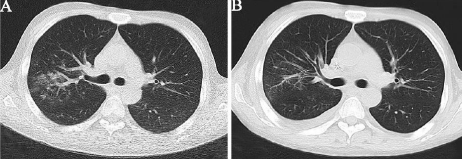
Figure 2: Different times of thorax CT images. A. The first thorax CT image
when suffering a worsening cough and fever; B. The infection was well under
control after the adjustments of treatment plan.
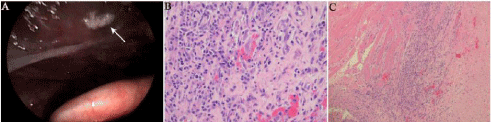
Figure 3: After 2 days of severe cough and fever, the patient developed severe
laryngeal edema, where a white pseudo-membrane attached to the left vocal
cord was observed under bronchoscopy (A). Hematoxylin-Eosinstain (H & E)
staining of granuloma lymphoid cells (B, magnification, ×400); HE staining of
rhabdomous granuloma necrosis (C, magnification, ×100).
Acknowledgement
This work was partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, grant 51703126), "Biomedicalengineering Cross Fund" of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (grant YG2017QN63), Youth Medical Talents-Medical Imaging Practitioner Program (SHWRS[2020]-087).
References
- Hamashima R, Uchino J, Morimoto Y, Iwasaku M, Kaneko Y, Yamada T, et al. Association of immune checkpoint inhibitors with respiratory infections: A review. Cancer Treat Rev. 2020; 90: 102109.
- Zimmer L, Goldinger SM, Hofmann L, Loquai C, Ugurel S, Thomas I, et al. Neurological, respiratory, musculoskeletal, cardiac and ocular side-effects of anti-PD-1 therapy. Eur J Cancer. 2016; 60: 210-225.
- Rizvi NA, Mazières J, Planchard D Stinchcombe TE, Dy GK, Antonia SJ, et al. Activity and safety of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, for patients with advanced, refractory squamous non-small-cell lung cancer from top to bottom (A-D) are consecutively 4 times of 18F-FDG PET/CT images. The MIP (A, B) demonstrated a focal activity (thin arrow) in the bilateral oropharynx. The soft tissue of oropharyngeal wall was extensively thickened (coarse arrow, A) and extended up and down to the left nasopharyngeal wall and larynx wall, and FDG metabolism was abnormally elevated (SUVmax:15.1).The imaging showed Complete Response (CR) from the patient after PD-1 treatment, suggesting satisfactory treatment efficacy (A, B, C). After the doctor adjusted the chemotherapy and anti-bacterial infection treatment, the patient was still showing a good response under a PET/CT scan (D). (CheckMate 063): a phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16: 257- 265.
- Wang H, Shao F, Li Q, Wu X, Jiang L. Bronchial inflammatory granulation after endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration and immunotherapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019; 46: 1199-1200.
- Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366: 2443-2454.
- Postow MA, Sidlow R, Hellmann MD. Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:158- 68.
- Wang DY, Salem JE, Cohen JV, Chandra S, Menzer C, Ye F, et al. Fatal toxic effects associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018; 4: 1721-1728.
- Schönrich G, Raftery MJ. The PD-1/PD-L1 axis and virus infections: a delicate balance. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019; 9: 207.
