
Research Article
Austin J Emergency & Crit Care Med. 2024; 8(1): 1072.
Metformin Attenuated Sepsis-Associated Myocardial Injury in Septic Rats
Niandan Hu; Bo Ai; Yongdong Ren; Hairui Chen; Wenqiang Li*
Department of Emergency, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
*Corresponding author: Wenqiang Li Department of Emergency, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China. Email: hu.niandan@whu.edu.cn
Received: April 17, 2024 Accepted: May 20, 2024 Published: May 27, 2024
Abstract
Objective: To study the effect of metformin on myocardial injury in septic rats.
Methods: Forty male Wistar rats were randomly allocated into four groups. In sham group, the cecum was turned over only after laparotomy and then returned to the abdominal cavity without CLP. Metformin (100mg/kg) was given to sham/M group rats 1.5 hours before laparotomy, the operation was the same as sham group. CLP group was treated with CPL for constructing the sepsis model. CLP/M group was treated with metformin (100mg/kg) gavage 1.5 hours before operation and CLP. Blood samples were collected for testing values of ALT AST CRE TNF-α IL-1β and cTnI in plasma by ELISA. TUNEL staining was used to detect the apoptosis of cardiomyocytes. Western blot was used to detect the expression of caspase-3 protein.
Results: Levels of ALT, AST, CRE, TNF-a, IL-1β and cTnI were not significantly difference between sham group and sham/M group. However, these biochemical parameters were significantly increased in the CLP group and CLP/M group, and the values were significantly decreased with a short-term treatment of metformin in CLP/M group compared to CLP group. Myocardial apoptosis indexes in CLP group and CLP/M group were significantly higher than that in sham group. However, apoptosis index in CLP/M group was significantly reduced than that in CLP group. Expression of caspase-3 protein was significantly higher both in CLP group and CLP/M group compared to sham group, and it’s significantly reduced in CLP/M group compared with CLP group.
Conclusion: Metformin demonstrates a protective effect in rats subjected to CLP model, particularly against myocardial injury. One possible mechanism underlying metformin’s mitigation of myocardial cell apoptosis in septic rats involves its ability to inhibit TNF-a production by activating AMPK. Additionally, metformin appears to suppress caspase-3 activity within the apoptosis cascade.
Keywords: Metformin; Sepsis; Myocardial injury; Apoptosis
Introduction
Sepsis refers to the uncontrolled response of the host to infection and life-threatening organ dysfunction [1]. Sepsis patients with myocardial injury will aggravate the evolution of the disease, which increase the risk of multiple organ failure and even death. Some studies reported that the mortality of sepsis patients with the myocardial injury can reach to 70%-90%[1]. At present, it is extensively believed that myocardial injury in sepsis is caused by the interaction of gene, molecule, metabolism, structure, autonomic nerve and hemodynamic changes [2,3]. The theory of "cytokine storm" in sepsis was gradually verified, which proposes that a large number of cytokines, chemokines and colony-stimulating factors had been produced and provided the basis for the occurrence and development of sepsis [4]. Metformin is a widely used first-line hypoglycemic drug. It can delay glucose uptake in the gastrointestinal tract, improve insulin sensitivity and inhibit gluconeogenesis, and reduce the activity of respiratory chain complex on mitochondria as well as reduce the production of ATP to activate AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) [5]. Recent studies found that metformin may reduce myocardial mitochondrial membrane potential by activating AMPK, thus reducing mitochondrial damage [6,7]. Therefore this study was designed to examine the effect of metformin on myocardial injury in septic rats.
Materials and Methods
Animals and Reagents
Experimental work on animals was performed in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and with approval of Animal Laboratory Center of Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University authorities. Male Wistar rats (180-200g, 4 weeks) were provided by Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention. The animals were randomly assigned to different experimental groups. Metformin was purchased from Shanghai Shiguibao Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.. TUNEL apoptosis detection kit was purchased from Roche Applied Science (Product No. 11684817910), and ELISA kits for TNF-a, IL-1β, cTnI were purchased from Wuhan YILAITE Biotechnology Co. Ltd. (Product No. E-EL-R0019c E-EL-R0012c E-EL-R1253c).
Grouping of Experimental Animals
40 rats were randomly assigned into 4 groups: sham group, sham/M group, CLP group and CLP/M group. In the sham group, the cecum was turned over only after laparotomy and then returned to the abdominal cavity without Cecal Ligation and Puncture (CLP). Metformin (100mg/kg) was given to sham/M group rats by gavage 1.5 hours before the operation, other operations were the same as sham group. CLP group was operated with CPL for constructing sepsis model. CLP/M group was treated with metformin (100mg/kg) 1.5 hours before operation and CLP.
Preparation of Sepsis Model in Rats
Sepsis model is caused by cecal ligation and puncture. Rats were anesthetized using 1.5% of isoflurane in air and the abdomen was shaved. And then rats were subjected to a longitudinal median laparotomy. Ligation was performed with No.4 silk thread 1 cm away from the blind end. Then, No.16 needle was used to penetrate the cecum twice at the distal end of the ligation site. After ligation and puncture, the cecum was returned to the abdominal cavity. And then the abdominal cavity was sutured. After the operation, saline 2ml/100g was injected subcutaneously to supplement the fluid loss during operation. The rats were sacrificed at 12 hours and 24 hours after the operation. Blood samples and tissue were collected and stored in a refrigerator at - 70°C. ALT, AST and CRE values were measured using biochemical methods. The concentrations of TNF-a, IL-1β and cTnI in plasma were measured by ELISA. Western blot was used to detected the expression of Caspase-3 protein in cardiomyocytes. The apoptosis of cardiomyocytes was detected by TUNEL method.
Statistical Analysis
All statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS21.0. The descriptive data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. The mean comparisons between groups were performed by one-way ANOVA. P values less than 0.05 were considered significant.
Results
Effects of Metformin on Plasma ALT, AST and CRE values
The plasma levels of ALT, AST and CRE increased at 12 hours and 24 hours after the operation. There were no significantly difference between sham group and sham/M group at 12 hours and 24 hours after the operation. The values of ALT, AST and CRE in CLP group and CLP/M group were significantly higher than in sham group at both 12 hours and 24 hours after the operation (P<0.05). However, CLP/M group had significantly lower values of ALT, AST and CRE than CLP group at 12 hours and 24 hours after the operation (P < 0.05) (Figure 1).
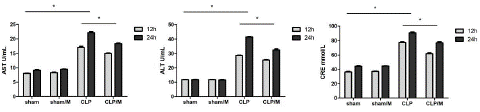
Figure 1: Effect of metformin on plasma ALT, AST and CRE values. The plasma values of ALT, AST and CRE were detected by biochemical methods. The results showed no significant changes between sham group and sham/M group at 12 hours and 24 hours after the operation. However, the values of ALT, AST and CRE in CLP group and CLP/M group were significantly increased compared to sham group at both 12 hours and 24 hours after the operation. Meanwhile, CLP/M group had significantly reduced values of ALT, AST and CRE than CLP group. (*P<0.05).
Effects of Metformin on Plasma TNF-a, IL-1β and cTnI Concentrations
There were no significantly difference in the concentrations of TNF-a, IL-1β and cTnI between sham group and sham/M group at 12h and 24h after the operation. The values of TNF-a, IL-1β and cTnI in CLP group and CLP/M group were significantly increased compared to sham group (P<0.05). But, the concentrations of TNF-a, IL-1β and cTnI in CLP/M group were significantly decreased than that in CLP Group (P<0.01) (Figure 2).
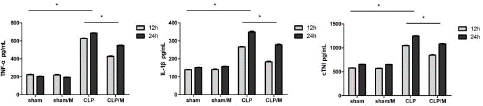
Figure 2: Effect of metformin on plasma TNF-a, IL-1β and cTnI concentrations. The concentrations of TNF-a, IL-1β and cTnI in plasma were measured by ELISA. There were no significant changes between sham group and sham/M group at 12 hours and 24 hours after the operation. But, the values of TNF-a, IL-1β and cTnI in CLP group and CLP/M group were significantly higher than that in sham group at both 12 hours and 24 hours after the operation. Meanwhile, CLP/M group had significantly decreased values of TNF-a, IL-1β and cTnI compared to CLP group. (*P<0.05).
Effect of Metformin on Apoptosis of Myocardial Cells
TUNEL staining was used to detect cardiomyocyte apoptosis 24 hours after operation. There was no significant difference in myocardial Apoptosis Index (AI) between sham group and sham/M group. The apoptosis indexes of myocardial cells in CLP group and CLP/M group was significantly higher than sham group (P<0.05). But, the AI of myocardial cells in CLP/M group was significantly decreased than that in CLP group (P<0.05) (Figure 3).
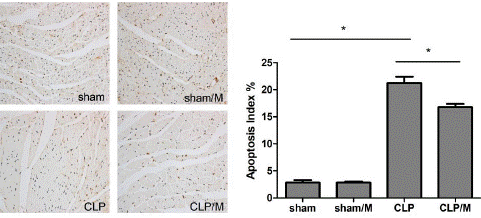
Figure 3: Effect of metformin on apoptosis of myocardial Cells. Cardiomyocyte apoptosis was detected by TUNEL staining. The apoptosis indexes of myocardial cells in CLP group and CLP/M group was significantly increased compared to sham group. However, the AI of myocardial cells in CLP/M group was significantly reduced than that in CLP group. (*P<0.05)
Effect of Metformin on Expression of Caspase-3 Protein
At 24 hours after operation, no significant differences were found in caspase-3 expression in cardiomyocytes between sham group and sham/M group. Compared with sham group, caspase-3 expression in CLP group and CLP/M group were significantly increased (P<0.05). However, the protein expression level of caspase-3 in CLP/M group was significantly reduced than that in CLP group (P<0.05) (Figure 4).
Discussion
Metformin is a widely used first-line hypoglycemic drug, which can significantly relieve the complications of type 2 diabetes and effectively improve the prognosis of diabetic patients[5]. Recently, a series of studies suggested that metformin not only has a hypoglycemic effect but also has remarkable anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-tumor, anti-aging and other pharmacological effects, which has extremely extensive clinical application range [5].
Studies have shown that metformin can inhibit the activity of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex, reduce intracellular ATP production, and increase the ratio of AMP/ATP and ADP/ATP [8], which may be the key cellular basis for metformin to exert its metabolic regulatory effects such as hypoglycemia [9]. The protective effect of metformin on acute myocardial infarction induced by isoproterenol was validated in the animal experiments, which mainly manifested by the reduction of myocardial fiber structure disorder, inhibition of inflammatory cell infiltration, and reduction of myocardial cell apoptosis and necrosis [10]. Therefore, metformin can play a protective role in diabetic cardiovascular complications, myocardial infarction and other pathological conditions. Our study found that cTnI concentration in plasma increased significantly in rat sepsis model caused by CLP which can be inhibited by administration of metformin. In addition, apoptosis indexes of myocardial cells was significantly reduced with a short-term treatment of metformin in CLP/M group which is compared to CLP group. The results were consistent with the previous findings and indicated that metformin had a protective effect on myocardial injury in sepsis.
In the study, we found that CLP induced myocardial injury was accompanied with increased inflammatory cytokines TNF-a and IL-1β. Related studies also demonstrated that TNF-a and other inflammatory cytokines participate in the process of sepsis-induced myocardial injury. TNF-a can directly inhibit myocardial contractility and lead to reversible ventricular enlargement [11]. This mechanism may be related to the activation of sphingomyelinase, proteolytic enzyme by TNF-a and the inhibition of calcium influx. Our study found that the plasma TNF-a level in CLP group was significantly increased than that in sham group. It’s further validating that TNF-a plays an important role in the process of sepsis-induced myocardial injury. Researchers found that activation of AMPK can inhibit endotoxin-induced TNF-a production in macrophages, while interference with AMPK expression can promote endotoxin-induced TNF-a expression [12]. It was also found that metformin significantly inhibited the plasma transaminase, the cascade activation of caspase and hepatocyte apoptosis, and a higher survival rate in mice with fulminant hepatitis induced by endotoxin [13]. These effects may be related to metformin inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic cytokines TNF-a [13]. Labuzek found that metformin can prevent myocardial cell death by activating AMPK, thus providing myocardial protection in sepsis [14]. The mechanism of action includes vasodilation, inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis proteins. Caspase-3 plays a key role in the activation of apoptosis cascade and it is important in the occurrence and development of cardiomyocyte apoptosis. According to Kewal Ramani’s study, AMPK can inhibit the activity of caspase-3, thus reducing the apoptosis of cardiomyocytes induced by TNF-a [15].
In this study, we found that apoptosis index of myocardial cells and the expression of caspase-3 protein in CLP group were significantly increased than that in sham group. However, apoptosis index of myocardial cells and caspase-3 protein expression could be significantly reduced in CLP/M group with administration of metformin than that in CLP group. These results indicated that as sepsis-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis leads to myocardial injury, metformin could effectively reduce myocardial cell apoptosis and alleviate myocardial injury caused by sepsis. The possible mechanism is that the production of TNF-a was inhibited by activating AMPK, meanwhile caspase-3 was also inhibited in the apoptotic cascade. It can reduce the apoptosis of myocardial cells and protect the myocardium. In conclusion, metformin can prevent myocardial injury in septic rats through inhibiting the production of TNF-a by activating AMPK and the activity of caspase-3 in the activation of apoptosis cascade.
References
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016; 315: 801-810.
- Merx MW, Weber C. Sepsis and the heart. Circulation. 2007; 116: 793-802.
- Kakihana Y, Ito T, Nakahara M, Yamaguchi K, Yasuda T. Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction: pathophysiology and management. J Intensive Car. 2016; 4: 22.
- Chousterman BG, Swirski FK, Weber GF. Cytokine storm and sepsis disease pathogenesis[J]. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. 39: 517-528.
- Campbell JM, Stephenson MD, de Courten B, Chapman I, Bellman SM, Aromataris E. Metformin Use Associated with Reduced Risk of Dementia in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018; 65: 1225-1236.
- El MS, Rongen GA, de Boer RA, Riksen NP. The cardioprotective effects of metformin. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2011; 22: 445-453.
- Caballero AE, Delgado A, Aguilar-Salinas CA, Herrera AN, Castillo JL, Cabrera T, et al. The differential effects of metformin on markers of endothelial activation and inflammation in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance: a placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89: 3943-3948.
- Vial G, Detaille D, Guigas B. Role of Mitochondria in the Mechanism(s) of Action of Metformin. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019; 10: 294.
- Yang Z, Kahn BB, Shi H, Xue BZ. Macrophage alpha1 AMP-activated protein kinase (alpha1AMPK) antagonizes fatty acid-induced inflammation through SIRT1. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285: 19051-19059.
- Soraya H, Rameshrad M, Mokarizadeh A, Garjani A. Metformin attenuates myocardial remodeling and neutrophil recruitment after myocardial infarction in rat. Bioimpacts. 2015; 5: 3-8.
- Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X, Fenyk-Melody J, et al. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest. 2001; 108: 1167-1174.
- Park CS, Bang BR, Kwon HS, Ai-Moon K, Kim TB, Lee KY, et al. Metformin reduces airway inflammation and remodeling via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012; 84: 1660-1670.
- Yuan H, Li L, Zheng W, Wan J, Ge P, Li H, et al. Antidiabetic drug metformin alleviates endotoxin-induced fulminant liver injury in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2012; 12: 682-688.
- Labuzek K, Liber S, Gabryel B, Okopien B. Metformin has adenosine-monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK)-independent effects on LPS-stimulated rat primary microglial cultures. Pharmacol Rep. 2010; 62: 827-848.
- Kewalramani G, Puthanveetil P, Wang F, Kim MS, Deppe S, Abrahani A, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase confers protection against TNF-{alpha}-induced cardiac cell death. Cardiovasc Res. 2009; 84: 42-53.