
Original Article
Austin J Cancer Clin Res. 2021; 8(1): 1089.
Identification of Novel GSK-3β Inhibitors through Docking Based Virtual Screening and Biological Evaluation
Xu M1#, Gao SY1#, Zeng YX1#, Xu L3, Gao JR1, Li J3, Zhou YB3*, Cheng G2* and Ye Q1*
1Zhejiang University of Technology, State Key Laboratory Breeding Base of Green Chemistry-Synthesis Technology, China
2Zhejiang Chinese Medicinal University, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, China
3National Center for Drug Screening, State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
#These two authors contribute equally
*Corresponding author: Yu-Bo Zhou, National Center for Drug Screening, State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Gang Cheng, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang Chinese Medicinal University, China
Qing Ye, State Key Laboratory Breeding Base of Green Chemistry-Synthesis Technology, Zhejiang University of Technology, China
Received: April 21, 2021; Accepted: May 11, 2021; Published: May 18, 2021
Abstract
GSK-3β is a key regulator in insulin, Wnt and NF-κB signaling pathways. Dysregulation of GSK-3β is often related to tumors and diabetes. Inhibiting it might provide cure for diabetes, tumors, neurodegeneration and brain ischemia. Although there are a number of reported GSK-3β inhibitors, the scaffold is limited. Herein we report a discriminatory analysis-based molecular docking on the Specs database, and identified 3 novel GSK-3β inhibitors with moderate IC50 (ranging from 17.42 μM to 6.74 μM) in the following in vitro biological test. Further dynamic simulations and docking pose analysis were performed to give a better understanding on the binding conformation of 3 hit compounds AK- 777/09836064, AK-968/37185006 and AN-698/41607072, which would provide basis for further optimization.
Keywords: GSK-3β inhibitors; Molecular docking; Virtual screen; Molecular dynamics
Introduction
Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine kinase family member, which was initially found to be one of the major rate-limiting enzymes in glucose metabolism. Glycogen synthesis can be inhibited by GSK-3 via phosphorylation of glycogen synthase [1,2]. However, studies over the past 20 years have shown that GSK- 3 is associated with multiple cellular functions including neuronal development [3], transcription [4], as well as cell division [5], survival and death [6,7]. GSK-3 has 2 major isoforms, i.e. GSK-3α and GSK- 3β. GSK-3β is an important component of multiple intracellular signaling pathways and is involved not only in the regulation of the insulin signaling pathway but also in others such as Wnt and NF- κB signaling pathways [8]. Development of many human diseases including diabetes [9], tumors [10], neurodegeneration [11], brain ischemia [12] is associated with abnormality in the regulation of the activity of GSK-3β. And thus, GSK-3β has emerged as a potential target for the treatment of a variety of diseases. The study of GSK-3β functional activity and the development of GSK-3β inhibitors have been actively pursuited. A number of GSK-3β inhibitors have been reported [13,14], and there are 3 main types: (ATP-) competitive inhibitor [15-21], non-competitive inhibitor [22,23] and substrate inhibitor [24-26]. Among them, LY2090314 [27] is an effective and selective ATP-competitive GSK-3 inhibitor for the treatment of acute leukemia, and is under phase II clinical trials for the treatment of leukemia [28]. The safety and effectiveness of 9-ING-41 as a single drug combined with cytotoxic drugs in refractory cancer patients is an ATP-competitive GSK-3 inhibitor currently in phase 1/2 [28]. Tideglusib is a non-ATP-competitive and irreversible GSK- 3β inhibitor, which is currently under phase II clinical trials for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease [28].
There are a number of GSK-3β inhibitors reported in literatures. However, most of them were restricted to have a five-membered heterocycle core and two aromatic rings. GSK-3β inhibitors with new scaffolds are needed. Computer-aided drug design has shown to be an effective approach to identify novel GSK-3 inhibitors [29]. Recently, various methods have been explored to improve the discriminatory ability of molecular docking [30-32]. Herein, we reported the identification of 3 novel inhibitors of GSK-3β from Specs database through a discriminatory analysis-based molecular docking and in vitro enzymatic experiment. Their IC50 values were determined as 6.74 ± 1.05, 17.42 ± 2.85, and 15.50 ± 1.57 μM, respectively. The binding mode of the most potent compound AN-698/41607072 was also investigated via molecular dynamic simulations, giving important information for further structural modification.
Results
Protein selection
To choose an appropriate PDB [33] structure, both crystal redocking analysis and comparable docking of inhibitors and decoys were performed for 30 protein chains. The resulting “RMSD” value and discrimination capability (p value) were listed in Table 1. Most PDBs successfully restore the near-native conformations of the inhibitors in the crystal complexes (RMSD<2.0Å), except for 2JDO_A, 3E87_A, 3 QKK_A, 3SAY_A, 4PTG_A and 5HLP_A. The discrimination power is the ability of molecular docking to distinguish the known antagonists from the decoys, which is more essential for a practical docking-based VS campaign. As shown in Table 1, half of PDBs have relative low p-value (lower than 1×10- 44), especially five complexes (1Q3D_A, 4PTE_A, 4PTG_A, 6Y9R_A and 6Y9S_A [34]) which have a p-value lower than 1×10-55. The best discrimination power was obtained with 6Y9S_A (p = 4.84×10-59). The docking scores for known inhibitors and decoys with the best two receptors (6Y9R_A and 6Y9S_A) were plotted in Figure 2, in which the known inhibitors (blue columns) could clearly be distinguished from the decoys (yellow columns). Therefore, 6Y9S_A were selected as the grid receptor for following virtual screening campaign.
Entry
Resolution(a) (Å)
crystal ligand re-docking(b)
discrimination capability
dock score
(p value)
1
1Q3D_A
2.2
0.4
-7.76
3.18×10-56
2
1Q3W_A
2.3
0.34
-9.11
1.65×10-46
3
1Q41_A
2.1
0.25
-10.71
1.35×10-48
4
1Q4L_A
2.77
0.3
-10.09
2.37×10-42
5
1Q5K_A
1.94
0.57
-7.53
8.76×10-54
6
1R0E_A
2.25
1.73
-10.47
1.10×10-38
7
2JDO_A
1.8
3.67
-8.09
2.55×10-12
8
2JDR_A
2.3
0.51
-11.53
6.22×10-34
9
2UW9_A
2.1
0.72
-10.08
1.10×10-14
10
2X39_A
1.93
0.88
-9.79
4.48×10-11
11
3CQU_A
2.2
0.98
-10.14
1.14×10-16
12
3CQW_A
2
0.44
-11.16
7.10×10-14
13
3DU8_A
2.2
0.4
-8.74
2.02×10-53
14
3E87_A
2.3
2.47
-10.2
1.12×10-16
15
3F7Z_A
2.4
0.63
-8.46
7.26×10-53
16
3GB2_A
2.4
1.34
-7.27
1.56×10-39
17
3QKK_A
2.3
4.63
-8.59
1.45×10-09
18
3SAY_A
2.23
7.18
-6.92
1.15×10-42
19
3ZRK_A
2.37
0.42
-7.84
2.44×10-47
20
3ZRL_A
2.48
0.29
-7.3
2.83×10-44
21
3ZRM_A
2.49
0.63
-7.34
2.88×10-54
22
4ACC_A
2.21
1.03
-8.35
2.98×10-52
23
4AFJ_A
1.98
0.47
-6.53
5.89×10-53
24
4PTE_A
2.03
0.38
-8.67
6.77×10-57
25
4PTG_A
2.36
2.06
-8.57
2.19×10-56
26
5HLP_A
2.45
2.49
-7.18
4.82×10-40
27
5KPK_A
2.4
0.9
-7.72
1.39×10-26
28
6V6L_A
2.19
1.3
-9.07
1.96×10-52
29
6Y9R_A
2.08
1.1
-9
1.07×10-59
30
6Y9S_A
2.03
0.55
-10.23
4.84×10-59
(a)The resolution of pdb structures. (b)re-dock using original ligand in receptor.
Table 1: Protein selection via crystal complex redocking analysis and discrimination capability for inhibitors and decoys by docking score.
Figure 1: GSK-3 inhibitors under clinical investigation.
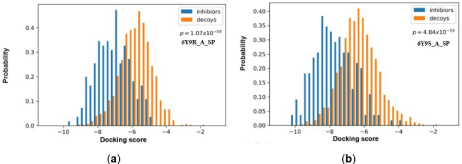
Figure 2: Distributions of the docking scores of GSK-3β for the two GSK-3β crystal complexes with the best discrimination power. (A) 6Y9R_A; (B) 6Y9S_A.
Docking-based virtual screening and enzymatic GSK-3β inhibition Assays
The prepared ligands from Specs compound library were docked with grid receptor 6Y9S_A. During docking process, the flexible ligand sampling with glide HTVS (high throughput virtual screening), glide SP (standard precision) or glide XP (extra precision) mode were applied in different stages [35]. To enhance the accuracy binding energy in late selecting stage, the docked conformations were used as the input files for evaluating Prime MM-GBSA (Molecular Mechanics/Generalized Born Surface Area) [36] energy. During the calculations, the protein flexibility was set to 5Å. Forming at least one hydrogen bond with WAL135 was another selecting criteria.
The structure-based virtual screening workflow was outlined in Figure 3A. Initially the prepared ligand molecules from Specs database [37] (http://www.specs.net, about 220,000 totally) were docked with grid receptor 6Y9S_A. To reduce computation cost, glide HTVS (high throughput virtual screening) process with flexible ligand sampling was applied at this stage. The resulting top HTVSscored 20000 compounds were then subjected to docking with the receptor in glide SP (Standard Precision) mode. At mean time, we noted that for most of 30 protein structure complexes, and the ligands have at least one H-bond with VAL135 (Figure 3C). Therefore, a pose filter rule of forming at least one H-bond with VAL135 was also used in this second step of virtual screen workflow to afford 1284 compounds. These compounds were further evaluated by glide XP (extra precision) mode and prime MM-GBSA rescoring and filtered through the criteria XP score < -7.23 and MMGBSA-dG < –51 to give 400 compounds. Afterwards, the 40 diverse compounds were picked by rdkit module based on Morgan fingerprint, and finally 10 compounds were selected manually by visual inspection with the following criteria: (1) Forming hydrogen bond with residue VAL135; (2) relative lower molecular weight. The 10 compounds were purchased and tested by in vitro enzymatic assay. And we were pleased to find three compounds (AK-777/09836064, AK-968/37185006, AN- 698/41607072) having inhibition rate more than 50%. The pairwise similarity (Tanimoto coefficient on Morgan fingerprint) of each identified ligand to each known was calculated using rdkit module [38]. The results were presented by violin plot as shown in Figure 3D. All three compounds were confirmed novelty, as similarity values are normally lower than 0.3, and highest similarity value is only up to 0.6. Further, the IC50 values for these three compounds were tested as 15.50 ± 1.57, 17.42 ± 2.85, and 6.74 ± 1.05 μM, respectively (Figure 4).
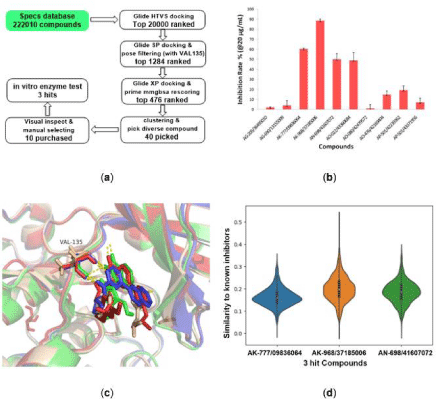
Figure 3: Virtual screening procedures and enzyme assays result for GSK-3β inhibition in vitro. (a) Protocol flowchart for discovery of GSK-3β inhibitor strategy
in this study. Numeral indicates the number of molecules in each stage. (b) Inhibitory activity of the 10 candidate molecules against GSK-3β protein at 20 μg/
mL. Staurosporine was used as a positive control and tested with an IC50 of 16.39 ± 0.14 nM. The red columnar bars represent the inhibition rate, and three hit
compounds showed more than 50% inhibition. (c) The aligned structures for 1Q41, 4PTE, 6Y9R and 6Y9S underlying the H-bonds of ligands with VAL135. This
is common for most of 30 PDB structures and here only list 4 representative PDB structures. Therefore forming at least one H-bond with VAL135 was applied as
a pose filter rule in second step of virtual screen workflow. (d) Violin plots of similarity (Dice similarity on Morgan fingerprint) for the 3 hits compound to the 2280
known GSK-3β inhibitors, suggesting all these 3 compounds are different from current inhibitors. The highest similarity is about 0.7.
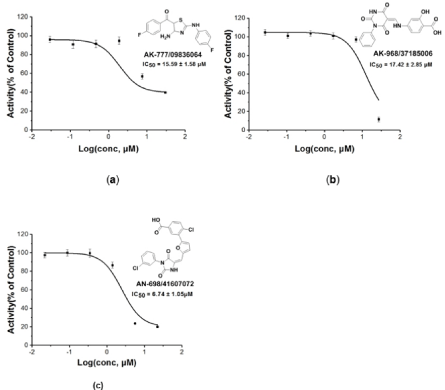
Figure 4: IC50 value curves for the three hit compounds.
MD simulations and interaction mechanism analysis
Molecular Dynamics simulations were carried out for the 3 hit compounds, the RMSD (Å) values curves of 8 ns simulations time were plotted (Figure 5A). These curves were stable after 0.5 ns which suggest that all 3 compounds could bind with the protein stably. Next, the energy decomposition was conducted by the MM/GBSA method, and the energy spectrum of inhibitor-residue interaction were shown in Figure 5B, 5C and 5D. Main residues which contribute relative higher energies were annotated by their residue name and number. ILE62, VAL135 and LEU188 were contributed significantly for all three compounds, especially VAL135. We inferred that hydrogen bonds with VAL135 might be essential for stable binding of protein and small molecules. Moreover, AK-968/37185006 and AN-698/41607072 shared quite similar spectrum (e.g. ILE62, VAL70, TRY134, VAL135, ARG141, LEU188 and CYS199), while the spectrum of AK-777/09836064 was quite different. This could be explained by 2.4 the binding poses of AK-777/09836064, AK- 968/37185006 and AN-698/41607072 with GSK3β.
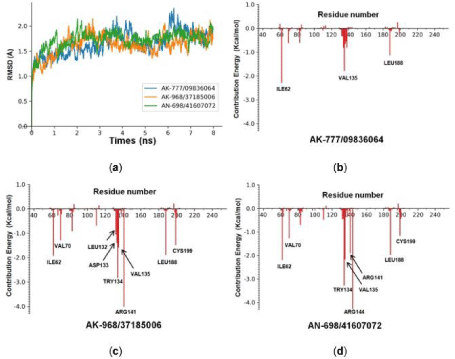
Figure 5: MD simulations and energy decomposition analysis of hits compounds with 6Y9S_A. (a) RMSD of 6Y9S_A backbone during the 8 ns simulation time. (b)
Binding energy contributions of the important residues of GSK-3β to AK-777/09836064. (c) To AK-968/37185006. (d) To AN-698/41607072.
To get a better understanding of the possible binding pattern for these 3 hits compounds, the docked poses of 3 hit compounds as well as the positive control compound (Staurosporine) were compared. As shown in Figure 6, all 4 compounds fit well in the ATP binding pocket of GSK3β, and form at least one hydrogen contact with VAL135. For Staurosporine (Figure 6a), one more hydrogen was generated between the NH of methylamine group with GLN85. While AK-777/09836064, AK-968/37185006, AN-698/41607072 have slight different orientations, the first two make additional hydrogen bond with ILE62, and the last one extends to other direction and forms two hydrogen bonds between its terminal carboxylic group with ARG144. Based on these observations, we deduce that the hydrogen bond contacts with VAL135 may play important role for above compounds, which would provide guidance in next round of modification for these hits compounds.
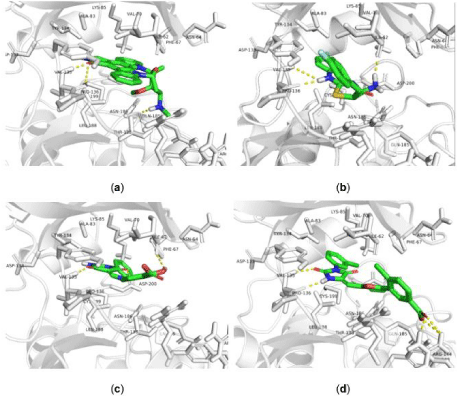
Figure 6: Predicted binding pose of GSK-3β (6Y9S_A) with Staurosporine and 3 hits compounds. (A) 6Y9S_A with Staurosporine with. (B) with AK-777/09836064.
(C) with AK-968/37185006. (D) with AN-698/41607072.
Materials and Methods
Database and protein preparation
Ligand Preparation. The small molecules library for virtual screen was downloaded from Specs database (http://www.specs.net) amounts to about 222010 [37]. Each compound were then treated by LigPrep module [39], including adding hydrogen atoms, removing the counterions, water and salts, tautomer generation and structure optimization based on the OPLS3 force field.
Apart from the small molecule database, 2280 known inhibitors (with IC50 values<10 μM) were obtained from ChEMBL Database [40] (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/), and 224 diverse compounds were picked by rdkit [38] according to MACCS fingerprint. Afterwards, the corresponding about 1117 decoys structures were built by DUD-E (http://dude.docking.org/) [41]. These inhibitors and decoys were processed by LigPrep module by the same methods as above.
Protein preparation
Currently 87 available X-ray crystal structures of GSK-3β complexed with inhibitors were deposited in the Protein Data Bank [33] (https://www.rcsb.org/), and their pdb format files were downloaded. More than half of the PDB IDs were removed, since there were no ligands or containing metal-chelated ligands, and 30 PDB structures were left. These protein structures were splitted into single chains, and each Chain A was selected and treated by Protein Preparation Wizard module [39] with default setting. Afterwards, the receptor grid files were generated via Receptor Grids Generation with default setting.
Protein selection
In order to select a proper crystal structure of GSK-3β for virtual screening, crystal ligand re-docking analysis of different grid receptors were conducted as well as comparable docking of inhibitors and decoys library. Each grid receptors gave two results, Root-Mean- Square Deviation (RMSD) and “discrimination capability” (Table 1). The value of RMSD from crystal ligand re-docking indicates whether the docking protocol can reproduce the ligand’s native conformation. For each processed GSK-3β complex, the ligand structure was extracted and re-docked back into its binding pocket by glide under Standard Precision (SP). A ideal protein was expected to have a RMSD value lower than 2 Å. Another key parameter for selecting docking protocols is the distinguish ability between known inhibitors and decoys (discrimination powers). 224 diverse known inhibitors and corresponding 1117 decoys were docking with each grid receptors by glide under Standard Precision (SP), respectively. Student’s t-test was also used to assess the significance of the difference between two sets of docking scores with the associated probability (p value). The better grid receptor for virtual screening was expected to have a lower p-value. After overall consideration of RMSD and discrimination capability (p value), 6Y9S_A (Chain A of PDB ID: 6Y9S [34]) was selected as the receptor for subsequent virtual screening (Table 1).
Molecular dynamics simulation
Molecular dynamics simulations were carried out for all the top 10 ligands with GSK-3β protein chain via Amber suite [42] following previously described protocols [43].
Enzymatic GSK-3β inhibition assays
The enzyme assay was conducted following previously described protocols [19].
Conclusion
In summary, docking-based virtual screening has been presented as a successful strategy for the identification of novel GSK-3β inhibitors. 6Y9S_A (PDB ID) was found as a suitable protein receptor for evaluating GSK-3β inhibitors from other compounds database. In addition, three compounds (AN-698/41607072, AK-968/37185006, AK-777/09836064), with micro-molar GSK-3β inhibitory potencies were identified from Specs database by tendem virtal screen and enzymatic assay. Moreover, the possible binding models of all three compounds with GSK-3β were discussed. All of these would provide a good basis for further structural optimization. We believe that our efforts could inspire future development of GSK-3β inhibitors.
Acknowledgment
In this section, you can acknowledge any support given which is not covered by the author contribution or funding sections. This may include administrative and technical support, or donations in kind (e.g., materials used for experiments).
Supplementary materials: The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1, the simi-larity of known GSK-3β inhibitors to 3 hits compounds and the inhibition rate of 10 tested com-pounds.
Funding
This study was financially supported by Project supported by the the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang (LY18H300009), the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (2014M550256), the State Key Laboratory of Drug Research (SIMM1601KF-04) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (8150131067).
References
- Woodgett JR. Molecular cloning and expression of glycogen synthase kinase-3/factor A. EMBO J. 1990; 9: 2431-2438.
- Harwood AJ. Regulation of GSK-3: A cellular multiprocessor. Cell. 2001; 105: 821-824.
- Hur E M, Zhou FQ. GSK3 signalling in neural development. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010; 11: 539-551.
- Hoeflich KP, Luo J, Rubie EA, Tsao MS, Jin O, Woodgett JR. Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta in cell survival and NF-kappa B activation. Nature. 2000; 406: 86-90.
- Cho J, Rameshwar P, Sadoshima J. Distinct Roles of Glycogen Synthase Kinase (GSK)-3 alpha and GSK-3 beta in Mediating Cardiomyocyte Differentiation in Murine Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284: 36647-36658.
- Beurel E, Jope RS. The paradoxical pro- and anti-apoptotic actions of GSK3 in the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis signaling pathways. Prog Neurobiol. 2006; 79: 173-189.
- Maurer U, Preiss F, Brauns-Schubert P, Schlicher L, Charvet C. GSK-3-at the crossroads of cell death and survival. J Cell Sci. 2014; 127: 1369-1378.
- Steinbrecher KA, Wilson W, Cogswell PC, Baldwin AS. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta functions to specify gene-specific, NF-kappa B-dependent transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 2005; 25: 8444-8455.
- Lee JS, Kim MS. The role of GSK3 in glucose homeostasis and the development of insulin resistance. Diabetes Res Clin Pr. 2007; 77: S49-S57.
- Cubrey JA, Steelman LS, Bertrand FE, Davis NM, Sokolosky M, Abrams SL, et al. GSK-3 as potential target for therapeutic irvention in cancer. Oncotarget. 2014; 5: 2881-2911.
- Takashima A. GSK-3 is essential in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2006; 9: 309-317.
- Valerio A, Bertolotti P, Delbarba A, Perego C, Dossena M, Ragni M, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition reduces ischemic cerebral damage, restores impaired mitochondrial biogenesis and prevents ROS production. J Neurochem. 2011; 116: 1148-1159.
- Aguilar-Morante D, Morales-Garcia JA, Sanz-SanCristobal M, Garcia- Cabezas MA, Santos A, Perez-Castillo A. Inhibition of Glioblastoma Growth by the Thiadiazolidinone Compound TDZD-8. Plos One. 2010; 5: 11.
- Bachmann RF, Schloesser RJ, Gould TD, Manji HK. Mood stabilizers target cellular plasticity and resilience cascades - Implications for the development of novel therapeutics. Mol. Neurobiol. 2005. 32: 173-202.
- Shin DK, Lee SC, Heo YS, Lee WY, Cho YS, Kim YE, et al. Design and synthesis of 7-hydroxy-1H-benzoimidazole derivatives as novel inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007; 17: 5686- 5689.
- Sivaprakasam P, Han X, Civiello RL, Jacutin-Porte S, Kish K, Pokross M, et al. Discovery of new acylaminopyridines as GSK-3 inhibitors by a structure guided in-depth exploration of chemical space around a pyrrolopyridinone core. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015; 25: 1856-1863.
- Tolosa E, Litvan I, Hoglinger GU, Burn D, Lees A, Andres MV, et al. A phase 2 trial of the GSK-3 inhibitor tideglusib in progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov Disord. 2014; 29: 470-478.
- Uehara F, Shoda A, Aritomo K, Fukunaga K, Watanabe K, Ando R, et al. 6-(4-Pyridyl) pyrimidin-4 (3H)-ones as CNS penetrant glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013; 23: 6928-6932.
- Ye Q, Shen YH, Zhou YB, Lv D, Gao JR, Li J, et al. Design, synthesis and evaluation of 7-azaindazolyl-indolylmaleimides as glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3 beta) inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2013; 68: 361-371.
- Zou HX, Zhou LY, Li YZ, Cui Y, Zhong HB, Pan ZY, et al. Benzo[e]isoindole- 1,3-diones as Potential Inhibitors of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3). Synthesis, Kinase Inhibitory Activity, Zebrafish Phenotype, and Modeling of Binding Mode. J Med Chem. 2010; 53: 994-1003.
- Fukunaga K, Uehara F, Aritomo K, Shoda A, Hiki S, Okuyama M, et al. 2-(2-Phenylmorpholin-4-yl)pyrimidin-4(3H)-ones, A new class of potent, selective and orally active glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013; 23: 6933-6937.
- Ser T, Steinwachs KC, Gertz HJ, Andres MV, Gomez-Carrillo B, Medina M, et al. Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease with the GSK-3 Inhibitor Tideglusib: A Pilot Study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013; 33: 205-215.
- Zhang P, Hu HR, Huang ZH, Lei JY, Chu Y, Ye DY. Identification of novel scaffold of benzothiazepinones as non-ATP competitive glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta inhibitors through virtual screening. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012; 22: 7232-7236.
- Hamann M, Alonso D, Martin-Aparicio E, Fuertes A, Perez-Puerto MJ, Castro A, et al. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3) inhibitory activity and Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) studies of the manzamine alkaloids. Potential for Alzheimer’s disease. J Nat Prod. 2007; 70: 1397-1405.
- Palomo V, Perez DI, Perez C, Morales-Garcia JA, Soteras I, Alonso-Gil S, et al. 5-Imino-1,2,4-Thiadiazoles: First Small Molecules As Substrate Competitive Inhibitors of Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3. J Med Chem. 2012; 55: 1645-1661.
- Tapia-Rojas C, Schuller A, Lindsay CB, Ureta RC, Mejias-Reyes C, Hancke J, et al. Andrographolide activates the canonical Wnt signalling pathway by a mechanism that implicates the non-ATP competitive inhibition of GSK-3 beta: autoregulation of GSK-3 beta in vivo. Biochem J. 2015; 466: 415-430.
- Kunnimalaiyaan S, Schwartz VK, Jackson IA, Gamblin TC, Kunnimalaiyaan M. Antiproliferative and apoptotic effect of LY2090314, a GSK-3 inhibitor, in neuroblastoma in vitro. BMC Cancer. 2018; 18.
- ClinicalTrials.gov is a database of privately and publicly funded clinical studies conducted around the world. 2020.
- Wang YX, Dou XD, Jiang L, Jin HW, Zhang LH, Zhang LR, et al. Discovery of novel glycogen synthase kinase-3 alpha inhibitors: Structure-based virtual screening, preliminary SAR and biological evaluation for treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Eur J Med Chem. 2019; 171: 221-234.
- Cheng G, Mei X, Yan YO, Chen J, Zhou Y. Identification of new NIK inhibitors by discriminatory analysis‐based molecular docking and biological evaluation. Arch Pharm. 2019; 352: e1800374.
- Pan P, Sun H, Liu H, Li D, Zhou W, Kong X, et al. In Silico Exploration for Novel Type-I Inhibitors of Tie-2/TEK: The Performance of Different Selection Strategy in Selecting Virtual Screening Candidates. Sci Rep. 2016; 6: 37628.
- Vieira TF, Sousa SF. Comparing AutoDock and Vina in Ligand/Decoy Discrimination for Virtual Screening. Appl Sci. 2019; 9: 4538.
- Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, et al. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000; 28.
- Buonfiglio R, Prati F, Bischetti M, Cavarischia C, Furlotti G, Ombrato R. Discovery of Novel Imidazopyridine GSK-3β Inhibitors Supported by Computational Approaches. Molecules. 2020; 25: 2163.
- Schrodinger LLC. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System. Version 1.8. New York, NY. 2015.
- Jakalian A, Jack DB, Bayly CI. Fast, efficient generation of high-quality atomic charges. AM1-BCC model: II. Parameterization and validation. J Comput Chem. 2010; 23: 1623-1641.
- Specs database. 2018.
- Landrum G. RDKit: Open-Source Cheminformatics. 2016.
- Schrödinger. Maestro, Version 9.0 Schrödinger LLC, New York, NY. 2009.
- Gaulton A, Hersey A, Nowotka M, Bento AP, Chambers J, Mendez D, et al. The ChEMBL database in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017; 45: D945-D954.
- Mysinger MM, Carchia M, Irwin JJ, Shoichet BK. Directory of useful decoys, enhanced (DUD-E): better ligands and decoys for better benchmarking. J Med Chem. 2012; 55: 6582-6594.
- Case DA, Rd CT, Darden T, Gohlke H, Luo R, Onufriev A, et al. The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J Comput Chem. 2010; 26: 1668-1688.
- Identification of Potential Inhibitors from Traditional Chinese Medicine for Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 Based on Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics Analysis. Chemistry Select. 2020; 5: 1248-1254.