Mini Review
Austin J Aquac Mar Biol. 2014;1(1): 3.
Current Status and Future Prospective for Aquaculture Sector in Turkey
Daniela Giannetto1*, Umit Acar2, Oguzhan Demir2 and Ali Turker2
1Department of Biology, Mugla Sitki Kocman University, Turkey
2Department of Aquaculture, Mugla Sitki Kocman University, Turkey
*Corresponding author: Daniela Giannetto, Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences, Mugla Sitki Kocman University, 48000 Kotekli-Mugla, Turkey.
Received: October 30, 2014; Accepted: December 11, 2014; Published: December 15, 2014
Abstract
In this paper a short review of the development of aquaculture in Turkey is provided. Due to its favorable geographic position between the Black Sea and Mediterranean Sea and a total sea coastline of 8483 km, Turkey holds a great potential for aquaculture. Turkish aquaculture industry has grown very rapidly, reaching great results in the European fish market for both marine and inland aquaculture. The most marine cultured species are European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) and, while inland aquaculture is mostly based on an intensive farming of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). In the last years a rapid increase in the export rates was registered and it exceeded the import. Despite this, there are still some aspects of Turkish fish production that need to be deepened in order to promote and add value to the national production.
Introduction
Worldwide production of fish products from aquaculture has showed a rapid grow in the last 20 years and currently it stands for nearly 50% of the global food fish consumption [1]. Fisheries and aquaculture strongly contribute to food supplies, occupation, export rates and income in national and local economies [2].
With decreasing of global capture fishery production and the concomitant increase of global population, aquaculture holds the highest prospective toward a future production of more fish to supply the increasing request for safe and value aquatic food [1]. Currently the most part of world aquaculture production is made in Asiatic countries (with China as the first producer) [3].
With a heritage of 200 natural lakes, 206 dam lakes, 952 man-make lakes, 33 rivers and 4 seas [4], Turkey owns a great potential for development of freshwater and marine aquaculture. The total Turkish coastline covers 8.483 km and climate, water resources and topography along the coasts create several suitable sites for marine cage culture [5].
Statistics on fisheries and aquaculture in Turkey are closely monitored by the Turkish Statistical Institute (TurkStat) since the 1967. The Institute has compiled statistics on sea products, fishing fleets and equipment every year. A web of correspondences among provinces (collecting records of provincial fish markets) and Ministry of Commerce allows the monitoring of Fisheries and Aquaculture activities in the country.
The rapid growth of aquaculture production in Turkey was certainly supported by a number of good governance decisions. In this contest, the "Aquaculture Regulation" (Regulation 25507), issued in 2004, represents the main benchmark, establishing the main set of laws related to the sector (i.e. site selection, changes and sales of farms; procedures for fish farming licenses; employment of technical work; management of fish well-being and health; monitoring of environmental impacts and its protection).
Since 2005 the government has started to endorse the aquaculture production by providing different kind of financial supports, namely a "premium payment" system correlated to the number of produced juveniles and marketed fish, financial credits with low interest rates, incentives and regional subsidies to support fisheries and aquaculture. Moreover, the preparation of site and area allocation plans, involving various stakeholders along the Mediterranean and Aegean coasts and the translocation of several marine farms from the near shore shallow waters to offshore areas, aimed to resolve conflicts between tourism and aquaculture. The main aims of these actions were to increase the production, promote the domestic consumption, avoid the production of unregistered or unlicensed products and develop environmentally friendly production systems.
Currently more than 12000 personnel in Turkey are employed in the aquaculture sector with the secondary support services (i.e. equipment, feed and consultancy) that provide job opportunities in the country [6].
The importance of Turkey in aquaculture is also underlined by the high number of institutions carrying on research on the sector: 18 fisheries Faculties, specific Departments in other Faculties and specific fisheries programs available at vocational high schools provide graduate and undergraduate instruction on aquatic sciences and fisheries. In addition, a Central Fisheries Institute associated with Ministry of Food, Agriculture & Husbandry is located in Trabzon (north east Black Sea coast of Turkey) and other 4 Fisheries Institutes were established in the country (2 of them in Isparta and Elazig focus on inland fisheries and farming) [4].
Short history of turkish aquaculture sector
The modern aquaculture activities in Turkey began in the 1960s with rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) cultured from eyed eggs imported from Italy. Marine aquaculture began in 1985 with the farming of European seabass (Dicentharchus labrax) and gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) from wild specimens caught from the sea (method that is no longer allowed).
The potential of aquaculture didn't reach big attention until the "anchovy crisis" in late 1980s, when a severe drop in the production of fish stocks in the Black Sea has led to pursuing new alternatives to the traditional fisheries. During early 1990s in the Black Sea some trials for the establishment of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) were carried on, but without a good success due to the high water temperatures of Black Sea during summer. In the last decade, the most important improvement for the sector was the implementation of bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) farming in Mediterranean and Aegean Sea. With regard to shellfish production, a limited farming of the Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovinciialis) has recently started in the Aegean Sea.
Nowadays Turkish aquaculture is characterized by limited species diversity: rainbow trout; common carp (Cyprinus carpio), gilthead sea bream, European seabass, blue-fin tuna, Mediterranean mussel and other species in small amounts, such as sharpn out sea bream (Diplodus puntazzo) and striped sea bream (Lithognathus olivieri) [7]. In order to enrich the farming diversity, experimental and pilot farming of alternative species are currently going on. For instance, some attempts toward the development of a commercial production of turbot (Psetta maxima), sturgeons (Acipenser spp) and native marine trout (Salmo trutta) were recently undertaken in Black Sea area [8].
With regard to the production systems, earthen ponds, concrete pools and off-shore cages are currently the most used in Turkey. Specifically, while the earthen ponds are used for production of carp and European seabass, concrete pools are employed for rainbow trout and off-shore cages are used for gilthead sea bream and European seabass.
Aquaculture production in turkey: current status
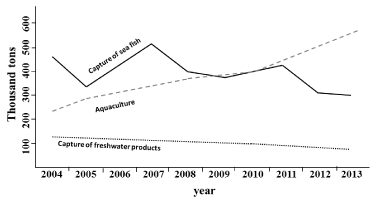
The Turkish aquaculture industry has experienced a notable progress in the last 10 years as underlined by the data reported in Figure 1: specifically, the farmed production in last 3 years exceeded the quantity of capture sea fish.

Figure 1: Trend of Turkish fisheries products industry in last 10 years (from [3] modified).
Data of aquaculture production from both marine and inland water showed an increment in the last 10 years (Figure 2), with the production of inland water exceeding the marine on the last 3 years.
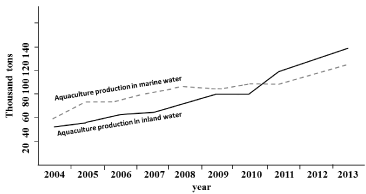
Figure 2: Trends of aquaculture production in marine and inland water (from [3] modified).
Considering only the data of 2013 (Table 1), the percentages of fish production in inland water gained the 52.71% against the 47.29% of marine. Analyzing the data of 2013 broken down by single species, the rainbow trout alone represented more than half (52.65%) of the total production in 2013 followed by the marine species European seabass (29.10%) and sea bream (15.30%). Among all, carp production is still scarce in Turkey since this species is mainly used for stock enhancement of lakes and reservoirs [5].
Type of production
Percentage
Inland water
52.71
rainbow trout
52.65
common carp
0.06
Marine water
47.29
marine brown trout
2.22
seabream
15.30
European Sea bass
29.10
Other
0.67
Table 1: Percentage of aquaculture production in 2013 (data from [3]).
Among the main cultured species, the production of rainbow trout currently represents the main source for Turkish aquaculture (followed by European sea bass) with an increasing trend of production in the last 4 years (Figure 3).
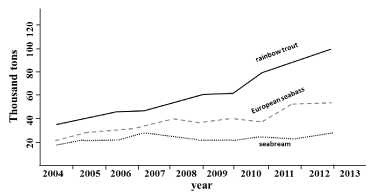
Figure 3: Trends of aquaculture production of the most cultured fish species (from [3] modified).
Currently, 1.935 licensed inland fish farms (with a capacity of 245.166 ton) against the 418 marine aquaculture facilities (total capacity of 217.166 tons) are known for Turkey [9]. While inland production derives almost from throughout the country, marine aquaculture is mostly concentrated on Aegean coasts (92% of sea farms) that possess the most suitable geographical and hydrographic conditions for the marine species farmed.
Trend of import, export and local consumption of aquaculture products
Data of trade of the Turkish fishery products showed a sharp increasing of export from 2010 reaching a maximum in the last 2 years (74 006 tons in 2012 to 101 062.8 ton in 2013) (Figure 4). About 80% of the European seabass and sea bream production is exported to European countries (Holland, Italy, Germany and Spain), Russia and Japan [3].
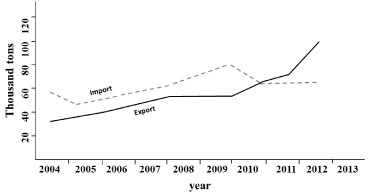
Figure 4: Trends of import and export of fishery products in Turkey (from [3] modified).
On the contrary, the trend of the import (mostly from Norway) remains almost stable in the last 3 years (65 698.4 in 2011 65 384 tons in 2012 and 67 530.2 in 2013).
Despite the positive trend of fish production, at present the annual fish consumption per capita in Turkey seems currently very low compared with that of most European countries and it showed a further decrease in the last 2 years (6.31 kg in 2013 against the 7.1 kg in 2012).
Conclusion
Turkey has a 25% market share as regards trade of European seabass and sea bream in Europe: it holds the first rank in the Mediterranean for European seabass farming and the second one (after Greece) for sea bream [10]. With regard to inland water farming, Turkey is also second (behind Norway) for the production of rainbow trout.
In recent times, the Aquaculture Producer's Association has been founded to provide support towards a development of aquaculture sector. Currently, the country has a significant know-how and research capacity, although an improved overall coordination of such activities is still required.
References
- FAO. Circular No. 1061/1 Regional review on status and trends in Aquaculture development in Europe. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture. 2010.
- Cattermoul B, Brown D, Poulain F, editors. Fisheries and aquaculture emergency response guidance Review recommendations for best practice. Food and Agriculture organization of The United Nations. FAO Workshop. 2013.
- TurkStat (Turkish Statistical Institute), - Statistical Yearbook. 2013.
- Gozgozoglu E, Deniz H, editors. Current Status of Aquaculture Progressed Developments, Encountered Problems and Actions for Solving the Problems in Turkey. Workshop on Determination of Environmental Impacts of Fish Farm to the Marine Ecosystem. 2014.
- Memis D, Demir N, Eroldogan OT, Kucuk S. Aquaculture in Turkey. The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture. Bamidgeh. 2002; 54: 34-40.
- European Commission. Studies to support the development of sea basin cooperation in the Mediterranean, Adriatic and Ionian, and Black Sea. 2014.
- Rad F, Koksal G, An overview of aquaculture in Turkey: with emphasis on sea bass and seabream. Aquaculture Economics & Management. 2000; 4: 227-240.
- Okumus I, Deniz H. Past, Present and Future of the marine aquaculture. Candan A, Karatas S, Kucuktas H, Okumus I, editors, In. "Marine Aquaculture in Turkey" Turkish Marine Research Foundation. 2007.
- Ministry of Food Agriculture and Livestock. General Directorate of Fisheries and Aquaculture. Fisheries Statistics. 2014.
- Deniz H, editor. Turkish aquaculture. 2nd Meeting of the COMCEC Agriculture Working Group. 2013.